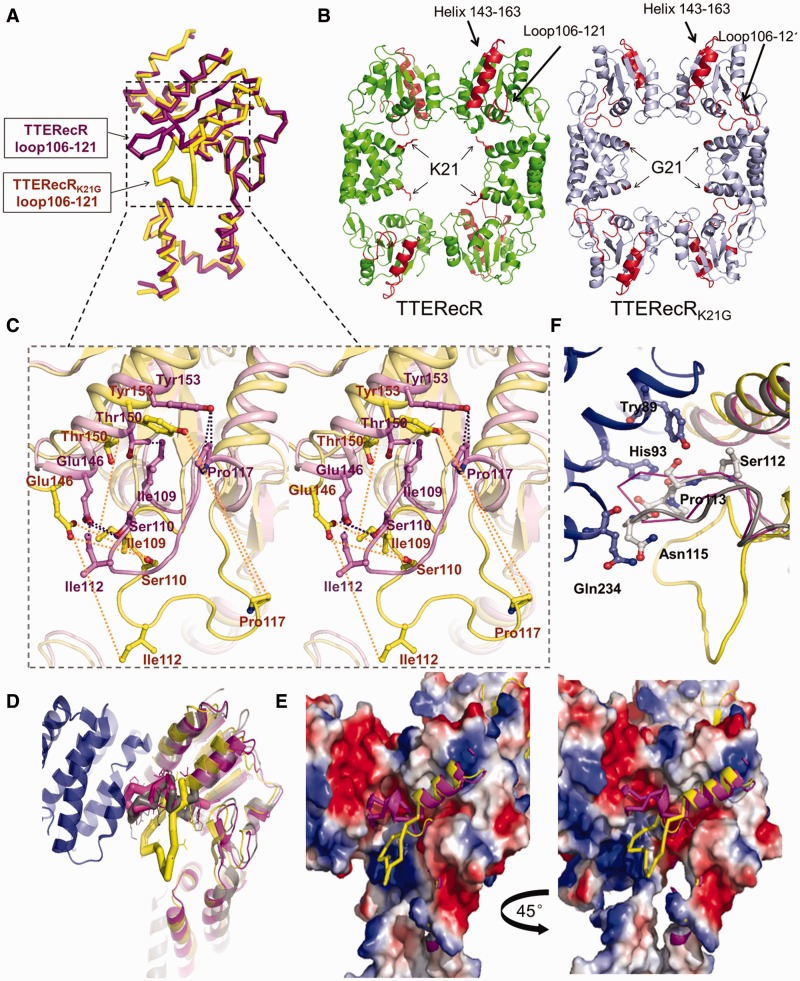
Figure 4.
Structure of TTERecRK21G. (A) Superimposed TTERecRK21G monomer (yellow) and TTERecR monomer (purple) structures as a ribbon diagram. (B) Comparison of the TTERecRK21G tetramer structure (light blue) with TTERecR tetramer structure (green). Lys 21 of TTERecR and Gly21 of TTERecRK21G are showed as sticks in red. Loop 106-121 and helix-α 143-163 is in red. (C) Superimposed TTERecRK21G (yellow) and TTERecR (purple) structures, wall-eyed view showing the interactions between the helix-α (residues 143-163) and loop106-121 are broken in the TTERecRK21G structure. Interacting residues are shown as sticks. (D) Superimposed structures of TTERecRK21G, TTERecR and drRecOR; drRecOR is coloured grey, other colours are as in A. (E) Electrostatic properties of the binding sites formed between TTERecRK21G or TTERecR and drRecO. The complexes are shown as solvent-accessible surfaces coloured by electrostatic potential contoured at ±5 Kt/e (red, acidic; blue, basic). (F) Loop 106-121 of TTERecR (purple) and drRecR (grey) interact with the hydrophobic pocket of drRecO (blue). Interacting residues are shown as sticks.