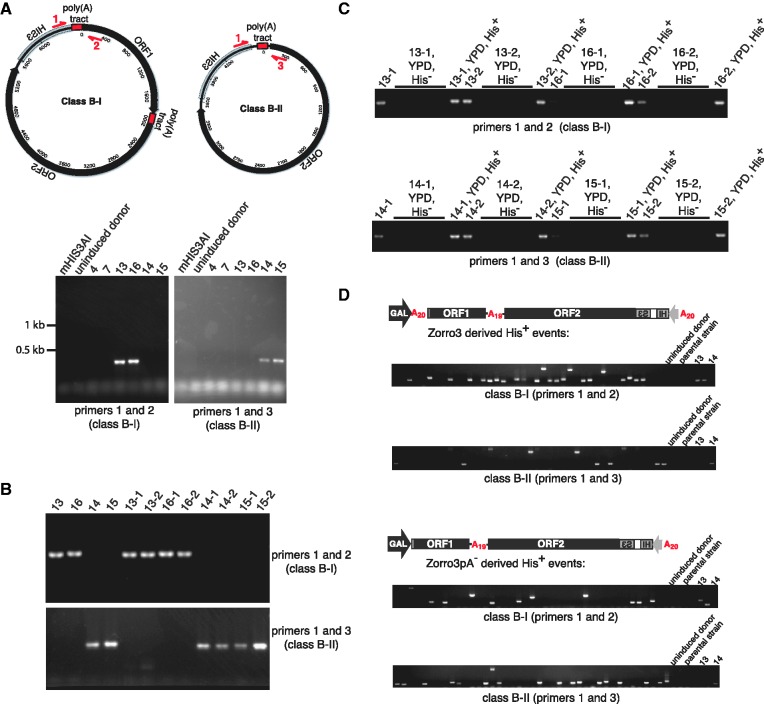
Figure 4.
Class B products form with high frequency. (A) A cPCR assay to detect class B products. The indicated primers (in red) were used for colony PCR reactions to specifically amplify products in strains containing class B-I or class B-II circles. (B) The cPCR assay is sensitive and specific for class B products. Original class B strains and strains converted to His+ by class B genomic DNA transformation (Figure 2C and D) were subjected to the cPCR assay. (C) His+ phenotype tracks with the class B circle. A His+ stability experiment (described in Figure 2E) was performed on parent strains transformed with a class B product. Colonies that lost the His+ phenotype (YPD, His−) and rare colonies that retained the phenotype (YPD, His+) were tested by the cPCR assay for the presence of a class B episome. (D) Class B products constitute the majority of Zorro3 retrotransposition events. For two strains (containing Zorro3mHIS3AI or Zorro3pA−mHIS3AI), 44 independently derived retrotransposition events (all unlabelled lanes) were tested by cPCR for the presence of class B-I or class B-II products. 13 = an original class B-I clone (control). 14 = an original class B-II clone (control).