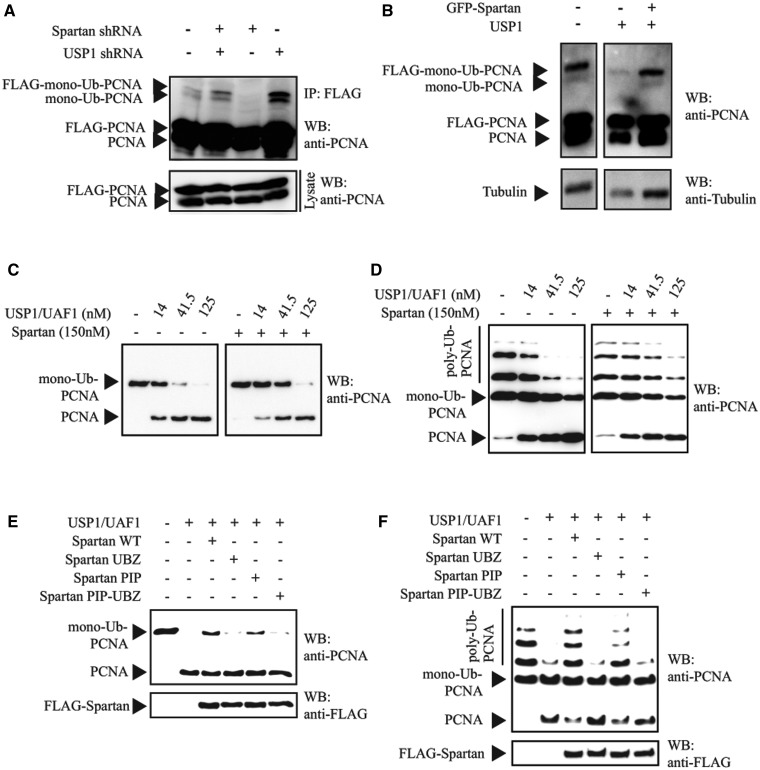
Figure 5.
Inhibition of the USP1-dependent deubiquitylation of ubiquitylated PCNA by Spartan. (A) USP1 knockdown reverses the reduction of PCNA monoubiquitination caused by Spartan knockdown. Spartan, USP1 and they together were knockdown along with transient expression of FLAG-PCNA in HEK 293 cells. After 24 h of transfection, cells were irradiated with 20 J/m2 UV, and in 3 h, cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. Monoubiquitylation of endogenous and FLAG-PCNA was detected by western blotting using anti-PCNA antibody. (B) Spartan overexpression reverses the reduction of PCNA monoubiquitylation caused by USP1 overexpression. HEK 293 cells were transfected with FLAG-PCNA and USP1 expression constructs together with mock or Spartan expression constructs. Cell extracts were prepared and analyzed as described in (A). (C) Spartan inhibits USP1-UAF1-dependent in vitro deubiquitylation of monoubiquitin-PCNA. Increasing amounts of purified USP1-UAF1 were incubated with purified monoubiquitin-PCNA in the absence (Lanes 1–4) or presence (5–8) of Spartan at 37°C for 45 min. Deubiquitylation of PCNA was analyzed on 10% denaturing polyacrilamyde gels followed by western blotting and visualization with anti-PCNA antibody. (D) Spartan inhibits USP1-UAF1-dependent in vitro deubiquitylation of polyubiquitin-PCNA. Analysis was carried out as in (A) but using purified polyubiquitin-PCNA substrate instead of monoubiquitin-PCNA. (E) The UBZ and PIP domains of Spartan are essential for inhibition of USP1-UAF1-dependent deubiquitylation of monoubiquitin-PCNA. Monoubiquitin-PCNA was incubated with USP1-UAF1 (50 nM) in the absence or presence of WT, UBZ, PIP or PIP-UBZ mutant Spartan proteins (150 nM). The reaction products were analyzed for deubiquitylation of monoubiquitin-PCNA by western-blotting using anti-PCNA antibody. (F) The UBZ and PIP domains of Spartan are essential for inhibition of USP1-UAF1-dependent deubiquitylation of polyubiquitin-PCNA. Analysis was carried out as in (C) but using purified polyubiquitin-PCNA substrate instead of monoubiquitin-PCNA.