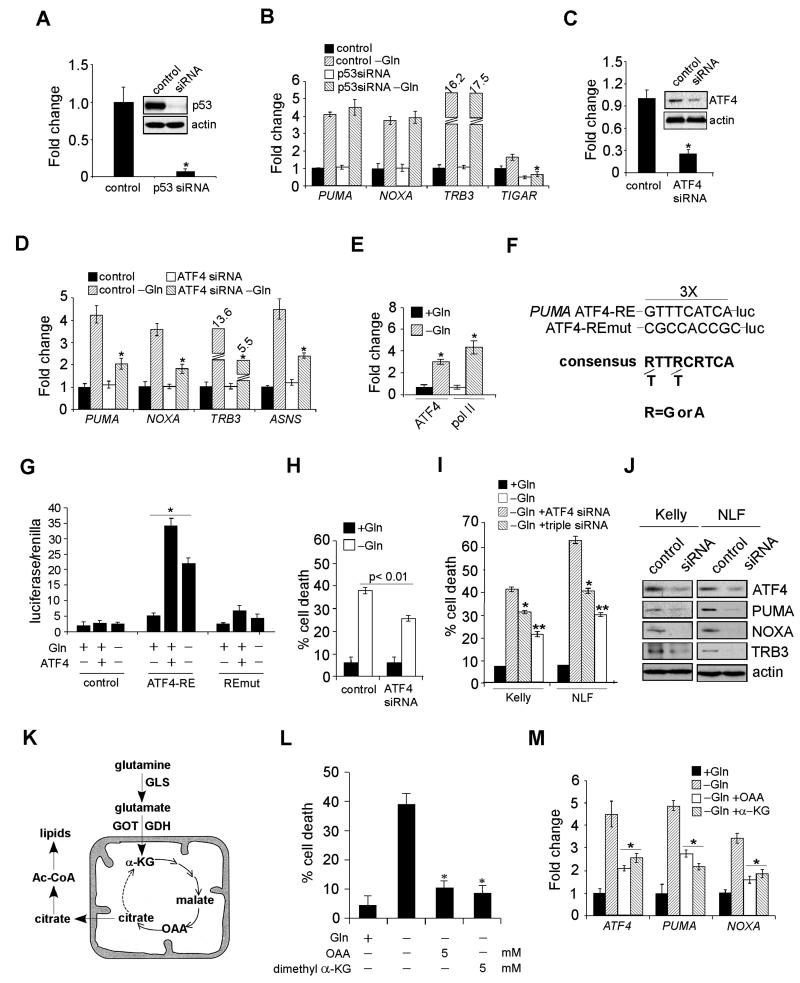
Figure 4. ATF4, but Not p53, is Responsible for PUMA, NOXA, and TRB3 Activation.
(A) Protein levels of p53 with or without siRNA knockdown.
(B) mRNA expression of indicated genes was examined by RT-PCR in Kelly cells transfected with a control siRNA or p53 siRNA in the presence or absence of Gln. Data are shown as an average of triplicates.
(C) Protein levels of ATF4 in Kelly cells with or without siRNA knockdown.
(D) Indicated gene expression was quantitated by RT-PCR in Kelly cells transfected with a control or ATF4 siRNA in the presence or absence of Gln. Data are shown as an average of triplicates.
(E) Specific chromatin binding of ATF4 evaluated by ChIP assay. Recruitment of Pol II was also assessed.
(F) Schematic representation of the consensus ATF4-binding site, the ATF4 response element (ATF4-RE) within the PUMA promoter and its mutant (ATF4-REmut).
(G) Luciferase assay was performed using control, ATF4-RE, and ATF4-REmut constructs with or without exogenous ATF4 expression or Gln starvation. Data are shown as an average of triplicates.
(H) Viability of Kelly cells transfected with a control or ATF4 siRNA in the presence or absence of Gln was examined by PI-Annexin V staining. Data are shown as an average of triplicates.
(I) Evaluation of Kelly and NLF cell death upon siRNA knockdown of ATF4 (using independent siRNAs from [C] and [H]), or a combination of PUMA, NOXA, and TRB3, in the absence of Gln.
(J) Western blots confirming the effect of siRNA knockdown in (I).
(K) Diagram depicting Gln metabolism in the TCA cycle. See text for more details.
(L) Evaluation of Gln-starved Kelly cell death upon the addition of OAA or α-KG.
(M) RT-PCR analysis of indicated genes in Kelly cells cultured in Gln-free or replete medium, or Gln-free medium supplemented with OAA or α-KG. Data are shown as an average of triplicates.
All error bars represent standard deviation. *p< 0.01. **p< 0.005. See also Figure S3.