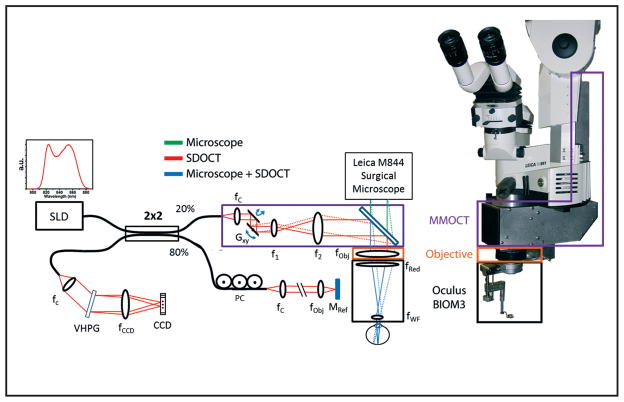
Figure 4.
Optical schematic and photograph of the microscope-mounted optical coherence tomography (MM-OCT) system mounted on a Leica surgical microscope. The optical paths of the surgical microscope (green) and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) (red) are shown along with the shared path (blue). The MM-OCT optics (purple box) consist of galvanometer scanners, a beam-expanding telescope, a dichroic beamsplitting mirror, and focusing optics from the surgical microscope including a microscope objective (orange box) and reduction and widefield ophthalmic lenses (black box). CCD = linear CCD array; PC = polarization controller; VPHG = volume phase holographic grating; SLD = super-luminescent diode; G = galvanometer.