Table 2.
Allylation of a variety of aryl halidesa
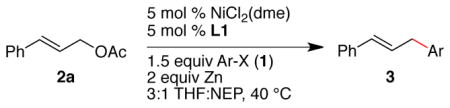
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | X | product | yieldb |
| 1 | I |
1 mmol scale, set up in glovebox |
88 |
| 2 | I | 10 mmol scale, set up on benchtopc | 81 |
| 3 | I |
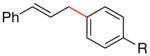 R = C(O)Me (3b) |
71 |
| 4 | I | R = CHO (3c) | 70 |
| 5 | I | R = NHTs (3d) | 73 |
| 6 | I | R = NHC(O)CF3 (3e) | 64 |
| 7 | I | R = CH2OTBS (3f) | 80d |
| 8 | I | R = NMe2 (3g) | 55 |
| 9 | I | R = Me (3h) | 86 |
| 10 | I | R = OMe (3i) | 83 |
| 11 | I | R = Br (3j) | 64e |
| 12 | Br | R = CO2Me (3k) | 65 |
| 13 | Br | R = C(O)Me (3b) | 48 |
| 14 | Br | R = CF3 (3l) | 51f |
| 15 | Br | R = CN (3m) | 77 |
| 16 | I |
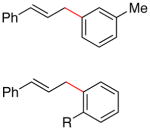 (3n) |
78 |
| 17 | I | R = CN (3o) | 86 |
| 18 | I | R = OMe (3p) | 80 |
As in Table 1, but on 1 mmol scale in 2 mL of THF/NEP. Reaction times were 15–24 h.
Yield after purification. For complete selectivity data, see Tables S1 and S2 in the Supporting Information.
A 1 mmol-scale reaction run on the benchtop (Procedure B) gave an 82% GC yield.
Reaction was run on a 0.5 mmol scale.
NMR yield of 3j. Isolated product is contaminated with 9% of 3a from hydrodeiodination.
Yield is an average of two runs, one at 0.5 mmol scale and one at 1 mmol scale.
