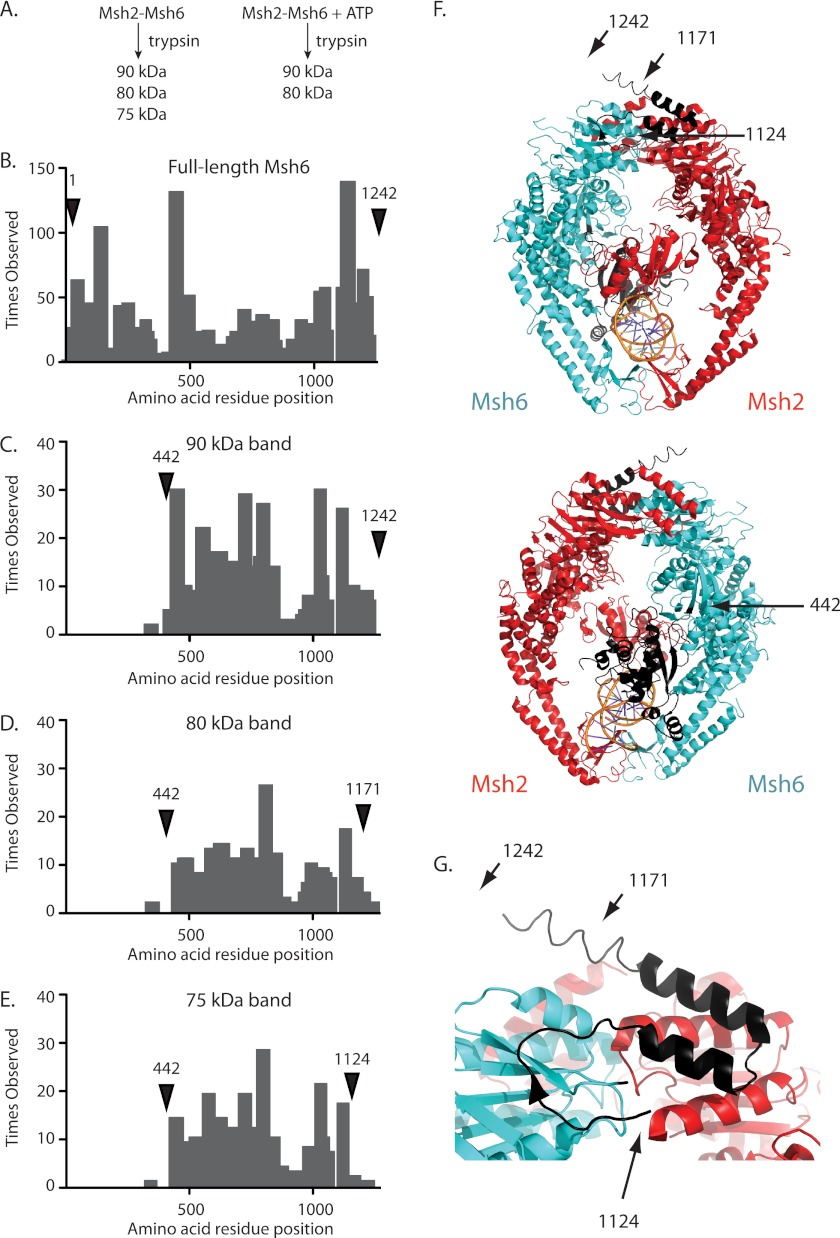
FIGURE 1.
Identification of the ATP-protected trypsin site in Msh6. A, the addition of ATP to a partial proteolysis reaction with Msh2-Msh6 prevents the generation of the 75-kDa fragment as previously demonstrated (41). B–E, histograms of the number of times each amino acid was observed by mass spectrometry for (B) full-length Msh6 and the (C) 90, (D) 80, and (E) 75-kDa trypsin fragments. Labeled arrows indicate the predicted N and C termini for each trypsin fragment. F, ribbon diagrams of human Msh2-Msh6 and bound mispaired DNA (Msh2, red; Msh6, blue; DNA, orange; PDB code 2O8B (39)) and the same structure rotated 180° generated with PyMol (59). The positions of the N and C termini of the 90-kDa fragment (residues 442–1242), 80-kDa fragment (residues 442–1171), and 75-kDa fragment (residues 442–1124) are indicated with arrows to the equivalent residues in human Msh6. G, expanded view of Msh6 C terminus with the C termini of the 90-, 80-, and 75-kDa fragments indicated with arrows.