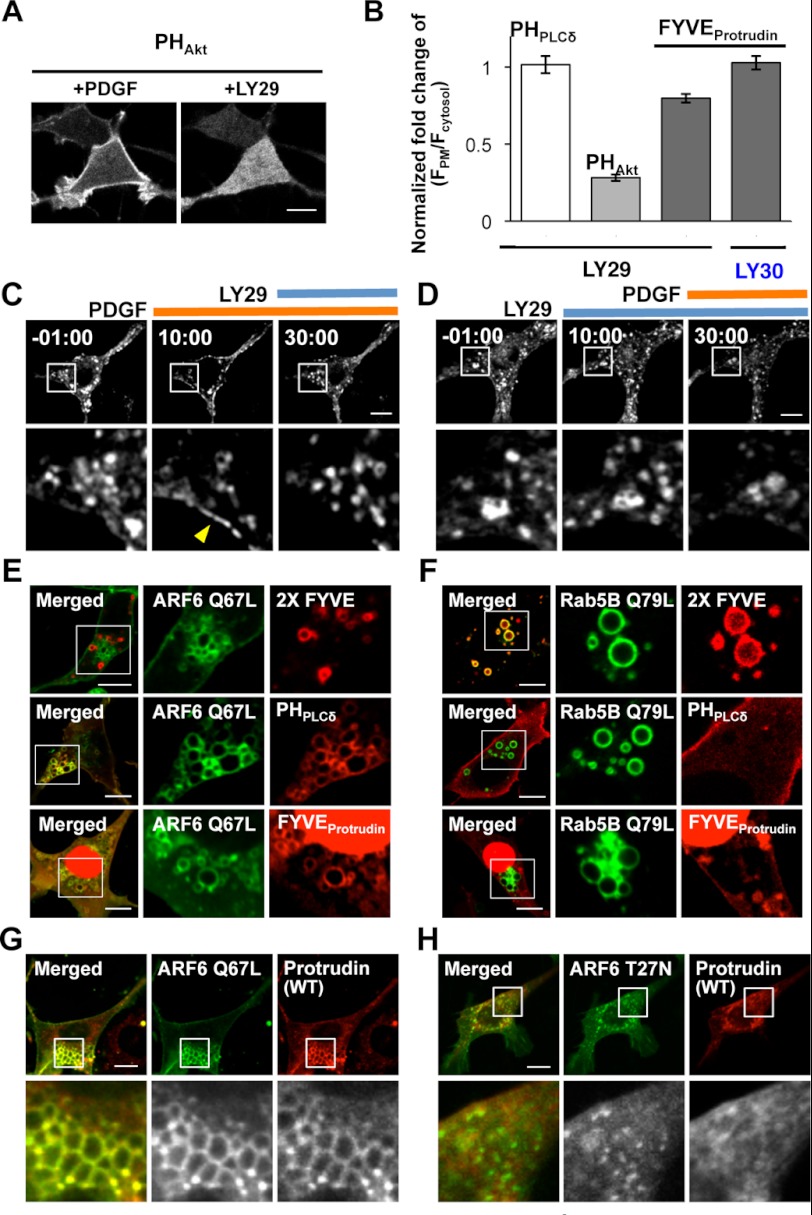
FIGURE 5.
The roles of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in protrudin localization through the FYVE domain. A, Akt-PH domain interacting PtdIns(3,4)P2 and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 stimulated by PDGF was completely removed from the PM under LY29. Bars, 10 μm. B, quantitative analysis of the level of controls, PLCδ-PH domain and Akt-PH domain, and protrudin-FYVE domain at the PM after LY29 or LY30 treatments. The fold-change of fluorescence intensity of each domain at the PM caused by chemical treatment was quantified as (F*PM/F*cytosol)/(FPM/Fcytosol), in which FPM/Fcytosol and F*PM/F*cytosol indicate the fluorescence ratio before and after each treatment, respectively. Error bars represent S.E. Cells expressing protrudin (WT) were sequentially treated with PDGF and LY29 (C) or vice versa (D). Yellow arrowhead indicates the PM. Bars, 10 μm. ARF6(Q67L)-EYFP (green) (E) or EYFP-Rab5B (Q79L) (green) (F) were cotransfected with the 2× FYVE domain (PtdIns(3)P biosensor, red), PLCδ-PH domain (PtdIns(4,5)P2 biosensor, red), and the protrudin-FYVE domain (red), respectively. ARF6(Q67L)-EYFP (green) (G) and ARF6(T27N)-EYFP (green) (H) were cotransfected with protrudin (WT, red).