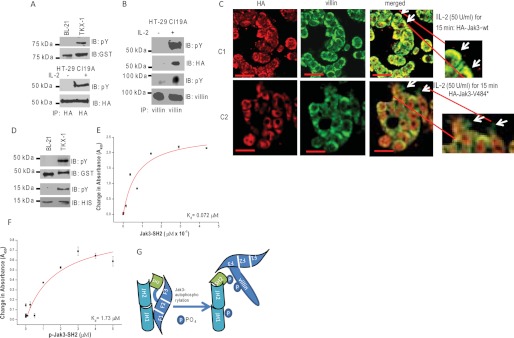
FIGURE 2.
Tyrosine phosphorylation of SH2 domain regulates the interactions between FERM domain of Jak3 and villin. A, tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak3-V484* in vitro and in human IEC. Western analysis of recombinant GST-Jak3-V484* (expressed and purified as in Fig. 1A) was done using pY20 (the top panel) and anti-GST (second from the top) antibodies. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak3-V484* in human IEC was determined by stable transfection of pCDNA-HA-Jak3-V484* into HT-29 Cl-19A cells treated with or without 50 units/ml of IL-2 for 15 min as reported before (8). Equal amounts of proteins from the cell lysates were subjected to IP using anti-HA antibody followed by IB using either pY20 (third from the top) or anti-HA (fourth from the top) antibody. B, tyrosine-phosphorylated Jak3-V484* interacts with villin in a human IEC. Similar experiments were done as in A, and the cell lysates were subjected to IP using anti-villin antibody followed by IB using pY20 (first and third from the top), anti-HA (second from the top), and anti-villin (the bottom panel) antibody. C–F, Jak3-V484* induces defective IL-2 functions in IEC. C, localization of HA-tagged Jak3-wt or Jak3-V484* and villin was examined in stably transfected HT-29 Cl-19A cells treated with IL-2 using IM as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Yellow color in the merged panels shows co-localization of HA-tagged protein and villin. Arrows indicate the defective periphery in cells expressing HA-Jak3-V484* (Scale bar-14 μm). D, GST-Jak3-G257* and His-Jak3-SH2 are tyrosine-phosphorylated. Similar experiments were done as in Fig. 1A to generate phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated proteins of GST-Jak3-G257* and His-Jak3-SH2. The expression and tyrosine phosphorylation of these proteins were detected through Western analysis using pY20 antibody (first and third from the top for JAk3-G257* and Jak3-SH2, respectively), anti-GST antibody (second from the top for GST-Jak3-G257*), and anti-His antibody (the bottom panel for Jak3-SH2). E and F, determination of Kd for His-Jak3-SH2 (E) or P-His-Jak3SH2 (F) binding to GST-Jak3-G257*. Similar experiments were done as in Fig. 1K to determine the Kd. G, proposed model for Jak3 interactions with villin. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the SH2 domain of Jak3 disrupts the interactions between the Jak3-FERM domain and Jak3-SH2 domain, making the F3 subdomain of the FERM domain available to interact with phosphorylated villin. A, B, and D, blots shown are representative of n = 3 with similar results. E and F, values are mean ± S.E. * indicates statistically significant differences from control (p < 0.05, n = 6).