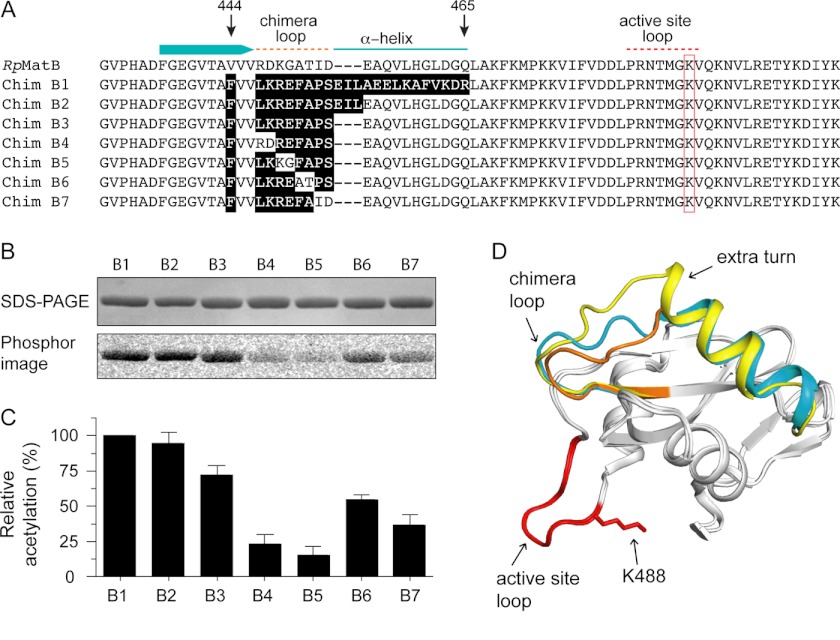
FIGURE 6.
Construction of a minimal RpMatB-BxBclM chimera. A, alignment of the C-terminal end of RpMatB, starting at residues 431, with the RpMatB-BxBclM chimeras (labeled B1–B7). Relevant secondary structure elements of RpMatB are shown above the alignment, and the red box indicates the active site lysine (Lys-488). Residues in the chimeras derived from BxBclM are highlighted in black. B, acetylation of each BxBclM chimera by RpPat using [1-14C]acetyl-CoA. C, amount of acetylation in B was quantified and normalized to the total acetylation of the RpMatB-BxBclM B1 chimera. Values represent averages and standard deviations of three experiments. D, alignment of the C-terminal domains of RpMatB and the RpMatB-BxBclM B1 and B3 chimeras. BxBclM-derived residues in the B1 chimera are indicated in yellow, BxBclM-derived residues in the B3 chimera are shown in orange, and the corresponding residues in wild-type RpMatB are shown in cyan. In all three structures, the catalytic loop and active site lysine are shown in red (lysine residue is modeled from the RpMatB apo structure). D was prepared with PyMOL (60).