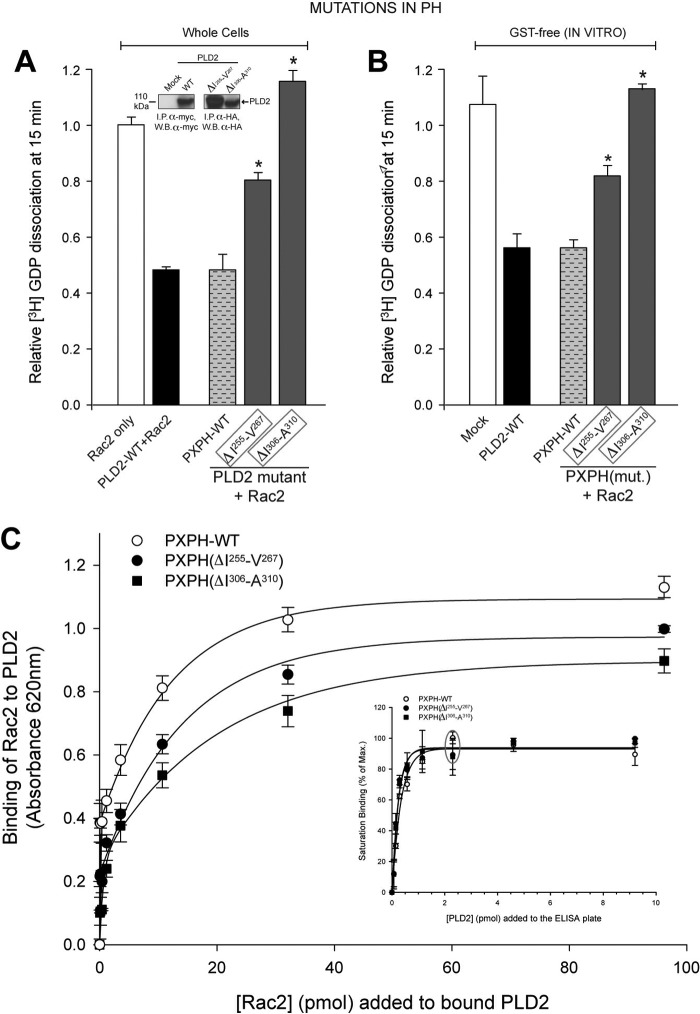
FIGURE 7.
Mutation analysis of PLD2 PH domain and the effect on its GEF activity. The PH point mutations were made in pcDNA3.1-mycPLD2 (full-length). Effects of mutation of PLD2 PH domain on Rac2 GDP dissociation from whole cells (first approach, immunoprecipitate (I.P.)-PLD2WT or mutants from COS-7 cells were analyzed for GEF activity using recombinant Rac2 as substrate) (A) or from purified, recombinant protein (second approach, purified recombinant PXPH with or without mutations in the PH domain along with recombinant Rac2 were used in the reaction mixture) (B). The residues targeted are Ile-255–Val-267 and Ile-306–Ala-310, as mentioned in Fig. 7. Mutants found to be involved in GEF activity in whole cells are outlined in gray boxes. The inset shows immunoprecipitation of representative myc-tagged mutants, verified by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. C and inset, Figure 5. PLD2 Rac2 binding is shown. The inset indicates that PXPH-WT or mutants were bound to ELISA plates until saturation (gray ellipse). Increasing amounts of baculoviral, purified HA-Rac2 (0.043–96.15 pmol) were laid on top of the PXPH-coated wells and bound Rac2 was detected with specific antibody. Protein binding was measured by spectrometry at A620 nm. Results represent the mean ± S.E. for four independent experiments.