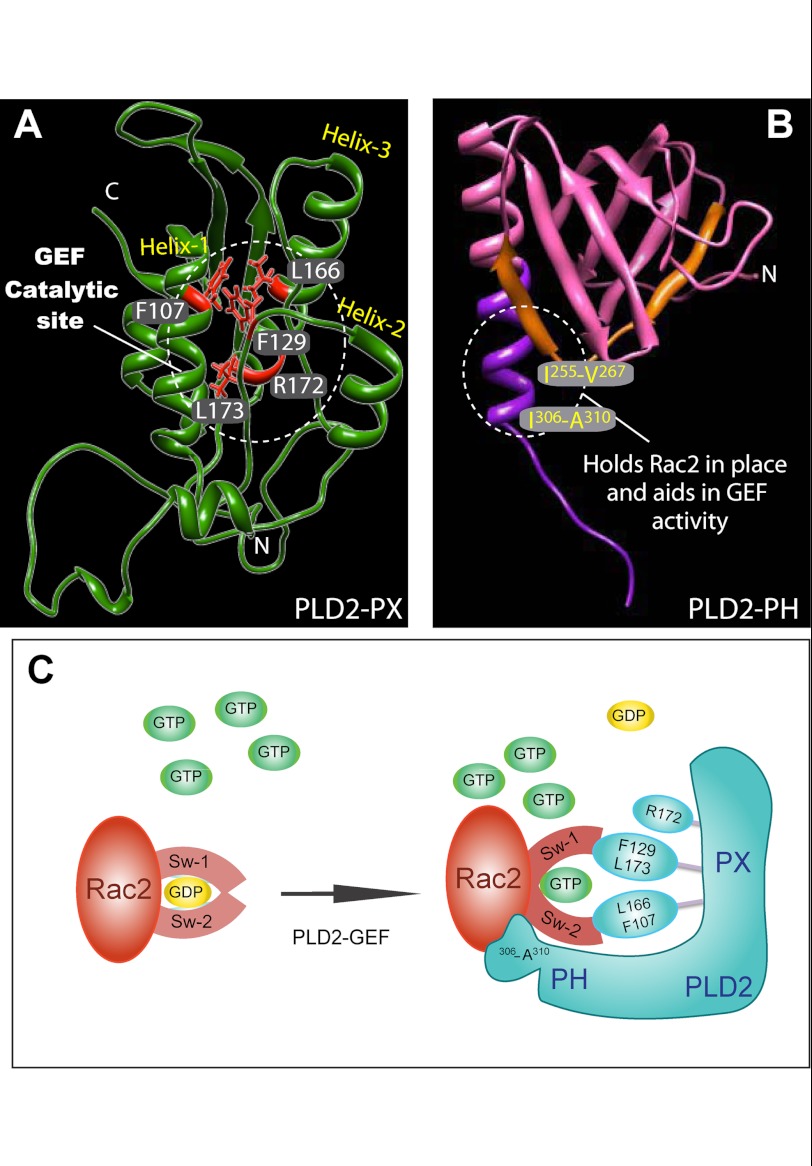
FIGURE 9.
Proposed GEF activity sites in PLD2 and the possible mechanism of action. A and B, shown are the proposed catalytic sites of PLD2 GEF activity according to this study. C, mechanism of PLD2-mediated nucleotide exchange is shown. Key residues on PLD2, phenylalanine 129, leucine 166, phenylalanine 107 and leucine 173 are shown as part of the catalytic site that forms a hydrophobic pocket. Phe-107 may need the interaction with an as-yet unknown cofactor in whole cells to function. In addition to this, arginine 172, the only charged residue, could aid in the GEF function. The model depicted in C indicates that Rac2 holds onto GDP with its switch 1 and 2 domains. PLD2 and Rac2 form a complex in such a way that switch 1/2 on Rac2 is perturbed, leading to GDP dissociation from Rac2. Followed by GTP binding to Rac2, switch 1/2 returns to the original conformation, leading to the separation of PLD2 from Rac2.