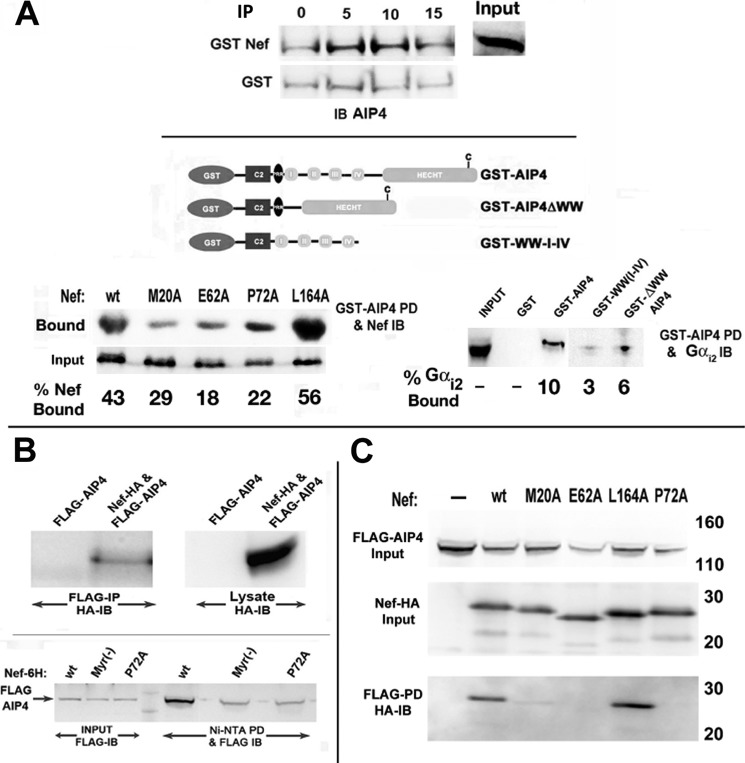
FIGURE 9.
Biochemical and genetic analysis of Nef interaction in vivo with Gαi2 and E3 ligases. A, Nef and Gαi2 interacted with AIP4 in vitro. Shown is a schematic illustration (top) of GST-tagged WT AIP4 and mutants deleted for the WW or HECT domains (44). Jurkat cells were transfected with WT, M20A, E62A, P72A, or L164A Nef mutant, and cellular extracts were incubated with ∼22 pmol of GST or GST-AIP4 immobilized on agarose beads. GST-bound fractions and unselected lysate (2%) were analyzed for Nef by immunoblotting (left). Cellular extracts of Jurkat cells were reacted with equimolar amounts (∼22 pm) of GST-AIP4, GST-AIP4 ΔWW, GST-WW-I-IV, or GST alone. Bound fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Gαi2 mAb (right). Input, an aliquot of extract immunoblotted without selection. Numbers in both cases refer to bound fraction (%) averaged from two experiments. B, in vivo interaction of Nef with AIP4. Extracts of Jurkat cells cotransfected with FLAG-AIP4 and HA-tagged Nef or empty HA vector and immunoprecipitated with FLAG-mAb and Nef were identified by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-HA (top). Relative binding affinity of Nef mutants for AIP4 was evaluated in Jurkat cells cotransfected with GFP, FLAG-AIP4, and His6-tagged WT or mutant Nef (bottom). Cellular extracts were bound to Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid beads, and the bound FLAG-AIP4 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG mAb. C, alternatively, Jurkat cells were cotransfected with GFP, FLAG-AIP4, and HA-tagged WT or mutant Nef. Extracts were immunoprecipitated with FLAG mAb, followed by immunoblotting with HA antibody. Data represent results from three experiments.