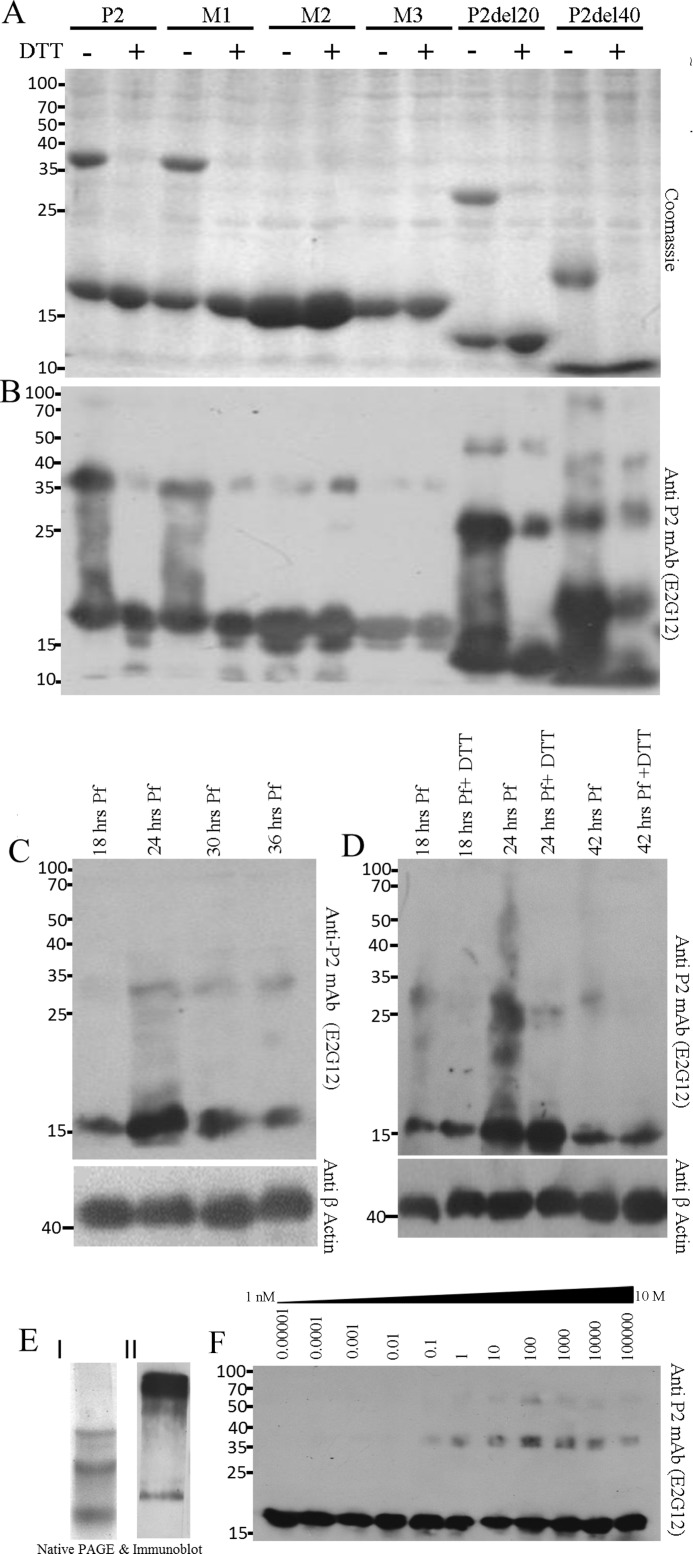
FIGURE 1.
P2 oligomerization of rPfP2 as well as in the Plasmodium parasite. A, Coomassie-stained gel of 2 μg of protein each of recombinant purified PfP2, PfP2 mutants M1 (C12A), M2 (C53Y), M3 (C12A,C53Y), PfP2 deletions P2del20, and P2del40 (supplemental Fig. S1) proteins were resolved on 12% SDS-PAGE in the absence and presence of reducing agent (10 mm DTT). B, the same gel in A was immunoblotted and probed with anti-PfP2 specific monoclonal antibody (E2G12) (24). C, about 4 μg each of parasite protein extract obtained from synchronized P. falciparum cultures harvested at 18, 24, 30, and 36 h post-merozoite invasion, were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent (10 mm DTT), and the immunoblot was probed using anti-PfP2 monoclonal antibody E2G12 (24). D, 4 μg of crude P. falciparum parasite protein harvested at 18, 24, and 42 h post-merozoite invasion were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE without and with reducing agent, 10 mm DTT, and the immunoblot was probed using anti-PfP2 monoclonal antibody E2G12 (24). β-Actin was used as a loading control. E, I, Coomassie stain of rPfP2 and II, immunoblot of 10 μg of asynchronous P. falciparum parasite crude protein extract, run on 10% native PAGE, and probed using anti-PfP2 monoclonal antibody (E2G12) (24). F, to estimate the concentration-dependent oligomerization, various concentrations of rPfP2 solution in PBS, pH 7.4, ranging from 0.01 ng/ml to 100 mg/ml were incubated at 4 °C for 48 h, and 1 ng of rPfP2 from each solution, diluted in SDS-PAGE loading buffer, was resolved on 12% SDS-PAGE with reducing agent (10 mm DTT) followed by immunoblotting and probing with E2G12 (24).