Purpose and Appropriate Sample Types
The present panel was constructed for the in-depth characterization of human T regulatory cells in both health and disease. The panel works well in both fresh and cryopreserved PBMCs (Table 1). The panel has also been tested on ACK-lysed peripheral blood. No other types of tissues have been tested.
Table 1.
Summary table for application of OMIP-004
| Purpose | Determine Treg levels and to provide an in depth characterization of Tregs |
| Species | Human |
| Cell types | Fresh or cryopreserved PBMCs, ACK-lysed blood |
| Cross reference | OMIP-001 |
Background
T regulatory cells (Tregs) are a subset of CD4 T cells, which are capable of suppressing immune responses of other T cells. In the peripheral blood of healthy individuals, these constitute approximately 3–5% of CD4 T cells. Tregs have been identified by a number of differing approaches, involving some, or all, of the following marker expressions: CD25high, Forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3), and CD127low (1–3). In the current panel, all of these markers were used, as well as additional markers such as CD39 that have been reported to be associated with high suppressive activity among Tregs (4). Antibodies to identify naïve and memory T cells, including CD45RA, CD27, and CD197 (CCR7) have been added to enable classification of Tregs in this manner (5–7). Finally, additional markers for gating (live/dead, CD45, CD3), and for cell activation (CD38, HLA-DR, CD103) were added to this panel (Supporting Information Table 2).
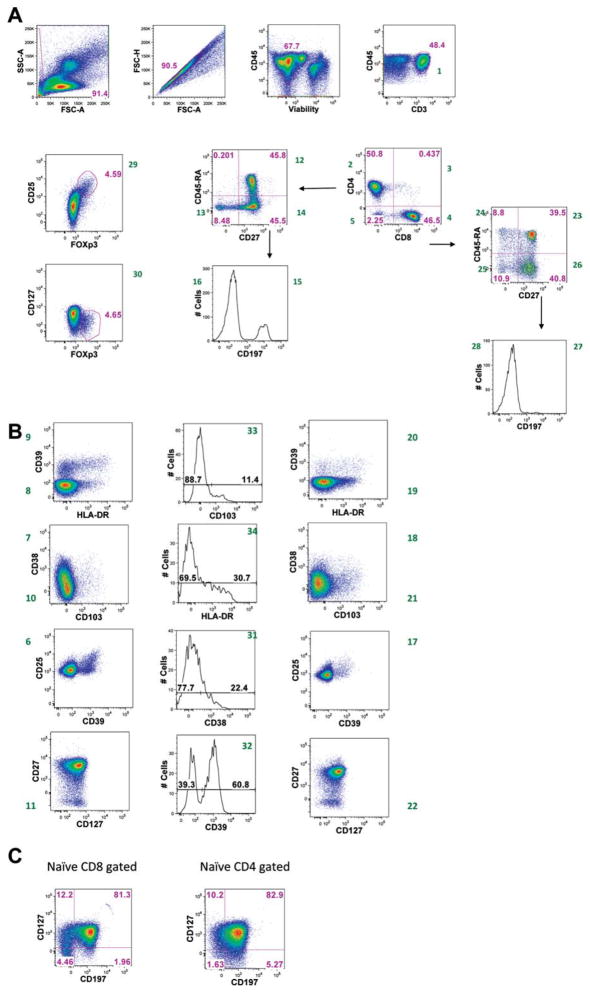
After testing several fluorochromes, R-phycoerythrin was reserved for FoxP3, as this marker was crucial for Treg identification. As this tube is part of a larger T cell panel with recurring markers, such as CD45, CD3, CD4 and CD8, an effort was made to assign these markers to fluorochromes that might not be widely available for other markers. Numerous clones and fluorochrome conjugates of antibodies were tested to optimize staining and minimize compensation (Supporting Information Table 3). FoxP3 is an intracellular antigen and requires the cells to be fixed and permeabilized for staining. This was performed after staining of the surface markers with the other antibodies. The use of the aqua blue live/dead stain still permitted exclusion of dead cells from analysis. Figure 1 illustrates the staining achieved with this panel, and a gating strategy that can be used to identify salient populations (Supporting Information Table 6).
Figure 1.
An example of staining patterns and gating strategies for all fluorescent parameters. PBMC were stained according to the OMIP-004 protocol. (A) Debris and doublets were excluded from analysis. Live mononuclear cells were selected for sequential analysis. T cells were identified by CD3 expression. T cells subsets were identified by expression of CD4 and/or CD8. The CD4 subset was examined for expression of CD25 and Foxp3. (B) Representation of remaining parameters, in CD8+ T cells (left), Treg (center) and CD4+ T cells (right). (C) Expression of CCR7 and CD127 on naive CD8+ (left) and naive CD4+ T cells (right). Naive cells were gated as indicated in Figure 1A, through CD45RA and CD27 bivariate dot plots. Numbers in green next to the dot plots are a reference to the populations reported in online Supporting Information Table 6.
As Tregs are a minor component of CD4 T cells in the peripheral blood, it is necessary to acquire a large number of cells to accurately enumerate the various Treg subsets encountered. It is desirable to acquire a minimum of 50,000 CD4 T cells for analysis, and substantially more if possible. Thus, data files resulting from running this tube generally contained between 300,000 and 1,000,000 events.
Similarity to Published OMIPs
This panel can be used to measure naïve and memory CD4 and CD8 populations in a manner similar to OMIP-001.
Supplementary Material
Table 2.
Reagents used for OMIP-004
| SPECIFICITY | FLUOROCHROME | CLONE | PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dead Cells | Aqua blue | na | Viability |
| CD45 | QD800 | HI30 | Leukocyte gating |
| CD3 | APC-Cy7 | Sk7 | T cell |
| CD4 | V450 | RPA-T4 | Helper subset |
| CD8 | QD605 | 3B5 | Suppressor subset |
| CD25 | PE-Cy7 | M-A251 | Treg gating |
| CD27 | QD655 | CLB-27/1 | |
| CD38 | PcP-Cy5.5 | HIT2 | |
| CD39 | AF488 | A1 | Treg suppression |
| CD45RA | PE-TR | 2H4LDH11LDB9 | Naïve |
| CD103 | PE-Cy5 | LF61 | |
| CD127 | AF647 | hIL-7R-M21 | Treg gating |
| CD197 | AF700 | 150503 | |
| HLA-Dr | PE-Cy5.5 | Tu96 | |
| FoxP3 | PE | PCH101 | Treg marker |
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mario Roederer, Pratip Chattopadhyay, and Steve Perfetto for their assistance in panel development, and Kristin Tarbell for her input regarding Treg markers.
Grant sponsor: NIH CHI Intramural Research Program.
Footnotes
This article is a US government work and, as such, is in the public domain in the United States of America.
Additional Supporting Information may be found in the online version of this article.
Literature Cited
- 1.Banham AH. Cell-surface IL-7 receptor expression facilitates the purification of FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:541–544. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Feuerer M, Hill JA, Mathis D, Benoist C. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells: Differentiation, specification, subphenotypes. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:689–695. doi: 10.1038/ni.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee MR, Zhu S, Gottlieb PA, Kapranov P, Gingeras TR, Fazekas de St, Groth B, Clayberger C, Soper DM, Ziegler SF, Bluestone JA. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J Exp Med. 2006;203:1701–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.20060772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mandapathil M, Lang S, Gorelik E, Whiteside TL. Isolation of functional human regulatory T cells (Treg) from the peripheral blood based on the CD39 expression. J Immunol Methods. 2009;346:55–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2009.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ahmed R, Bevan MJ, Reiner SL, Fearon DT. The precursors of memory: Models and controversies. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:662–668. doi: 10.1038/nri2619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Appay V, van Lier RA, Sallusto F, Roederer M. Phenotype and function of human T lymphocyte subsets: Consensus and issues. Cytometry A. 2008;73:975–983. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Song K, Rabin RL, Hill BJ, De Rosa SC, Perfetto SP, Zhang HH, Foley JF, Reiner JS, Liu J, Mattapallil JJ, Douek DC, Roederer M, Farber JM. Characterization of subsets of CD4+ memory T cells reveals early branched pathways of T cell differentiation in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:7916–7921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409720102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.