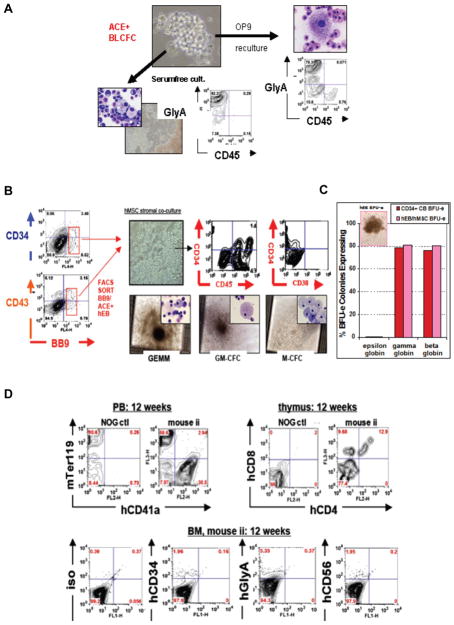
Fig. 3. Generation of short-term engrafting he-matopoietic progenitors from hESC-derived hemangioblasts.
(A) Clonogenic human blast colony-forming cell (BL-CFC) assays of hEB-derived ACE+ hemangioblasts. Clonal blast colony formation (BL-CFC assays) from single Line H1 (WA01) hEB cells was tested and optimized in serum-free (SF) methylcellullose medium using growth factors known to expand mouse BL-CFC. Human blast colonies expanded from day 6–10 hEB, and minimally required VEGF, FGF2, and TPO to proliferate. Mature blast colonies differentiated into clusters of multipotent primitive-definitive CD43+CD45+CD41+ progenitors, and contained clonal progenitors for primitive YS-like GlyA+ CD45− erythroid cells and endothelium following reculture into serumfree and stromal-free culture conditions; or definitive GlyA+ CD45+ erythro-my-eloid cells if alternatively cultured on OP9 bone marrow stromal layers. Figure adapted from Zambidis et al., 2008, with permission. (B–D) Generation of engraftable CD34+CD45+CD38− adult-type definitive-type he-matopoietic progenitors from ACE+ hEB-derived human hemangioblasts following in vitro maturation on mesenchymal stro-mal niches, or in vivo injection into mouse neonatal livers. (B) Day 9 to 10 FACS-sorted ACE+ CD34+ and ACE+ CD43+ hEB populations (from Line H1 (WA01)) containing hemangioblasts were cultured on human mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSC), and supplemented with human hematopoietic growth factors. This co-culture system differentiated YS-like ACE+CD34+ hEB cells into ” cobblestone ” - appearing CD34+CD45+CD38− cells that generated abundant definitive CFU in meth-ylcellulose assays (GEMM-CFC, GM-CFC, and M-CFC shown, as well as G-CFC, BFU-e, CFU-e) that were indistinguishable from CD34+ cord blood (CB) control colonies. (C) These hEB-derived erythroid CFU resembled CB BFU-e in morphology and adult hemoglobin expression with low intracyto-plasmic embryonic globin (epsilon), and high amounts of fetal (gamma) and adult globin (beta) expressions. (D) Analysis of in vivo maturation of hEB-derived cells following injection of stroma-differentiated hEB into the neonatal liver of highly immunodeficient, irradiated (150 Gy) NOD/SCID/IL2Rgnull(NOG) mice (n=4). At 12 weeks, there was evidence for multi-lineage lympho-erythro-myeloid engraftment; peripheral blood (PB) FACS analysis detected high levels of mouse erythroid marker Ter119 and human CD41a (hCD41a), a megakaryocyte marker. Double positive hCD4+CD8+ hematopoietic cells in the thymus demonstrated mature T cell maturation/engraftment, while low levels of detectable hCD34, hGlycophorin A (CD235a), and hCD56 were found in the bone marrow of transplanted NOG mice.