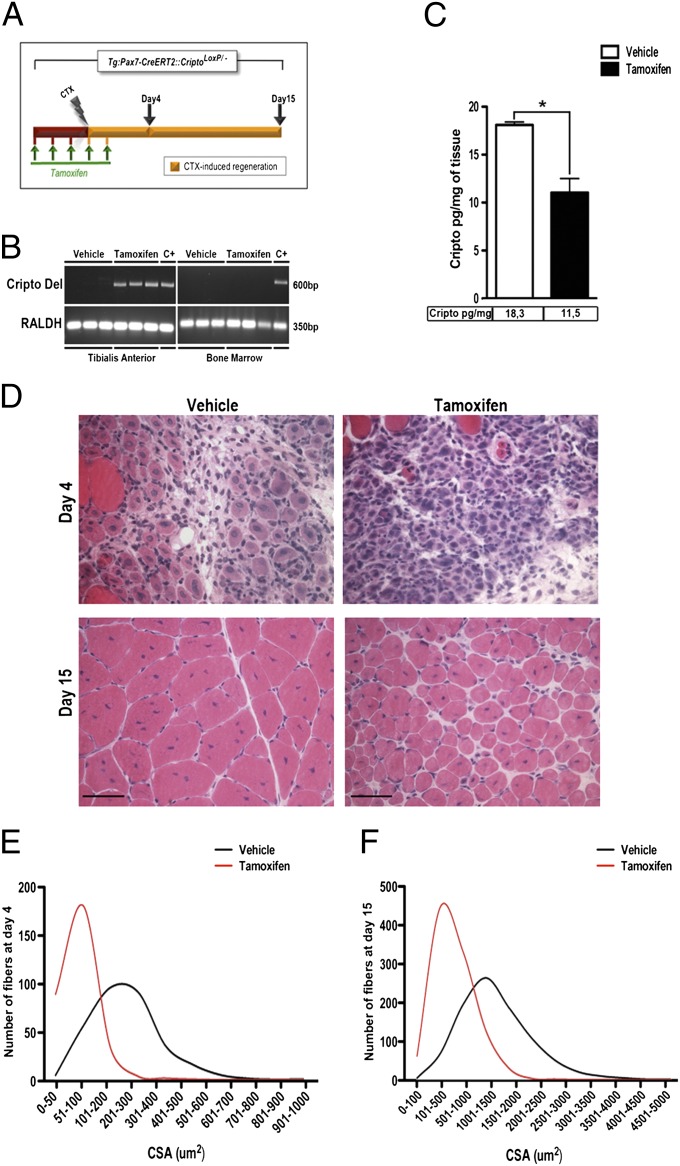
Fig. 3.
Conditional targeted deletion of cripto in satellite cells impairs muscle regeneration after acute muscle damage. (A) Schematic representation of conditional loss of function of Cripto using Tg:Pax7-CreERT2::CriptoloxP/− mice. Tamoxifen or control vehicle was injected i.p. in adult mice (1 mo of age) once a day for 5 d. At day 4, regeneration was triggered by CTX injection in TA muscle of both groups, and analysis was performed at the indicated time points (day 4 and day 15). (B) PCR analysis shows tamoxifen-induced deletion of Cripto floxed allele (Cripto Del) only in uninjured contralateral TA muscle (Left) but not in bone marrow (Right), isolated at day 15. Genomic DNA isolated from uninjured TA muscles and bone marrow of tamoxifen-treated CriptoloxP/loxP CAG-CreERT2 mice was used as a positive control (C+). RALDH, retinaldehyde dehydrogenase. (C) ELISA-based assay of Cripto protein levels in muscle tissue of Tg:Pax7-CreERT2::CriptoloxP/− mice treated with either sesame oil as a control or tamoxifen at day 4 after injury (18.1 ± 0.3 pg/mg for control vs. 11.05 ± 1.4 pg/mg for tamoxifen). Values are mean ± SEM; n = 3 mice per group; *P = 0.04. (D) Representative H&E-stained sections of CTX-treated muscles at indicated time points. (Scale bars = 50 μm.) CSA analysis of regenerated fibers at day 4 (E) and at day 15 (F) shows smaller myofibers in tamoxifen treated mice vs. control mice at both time points. See also Table S1.