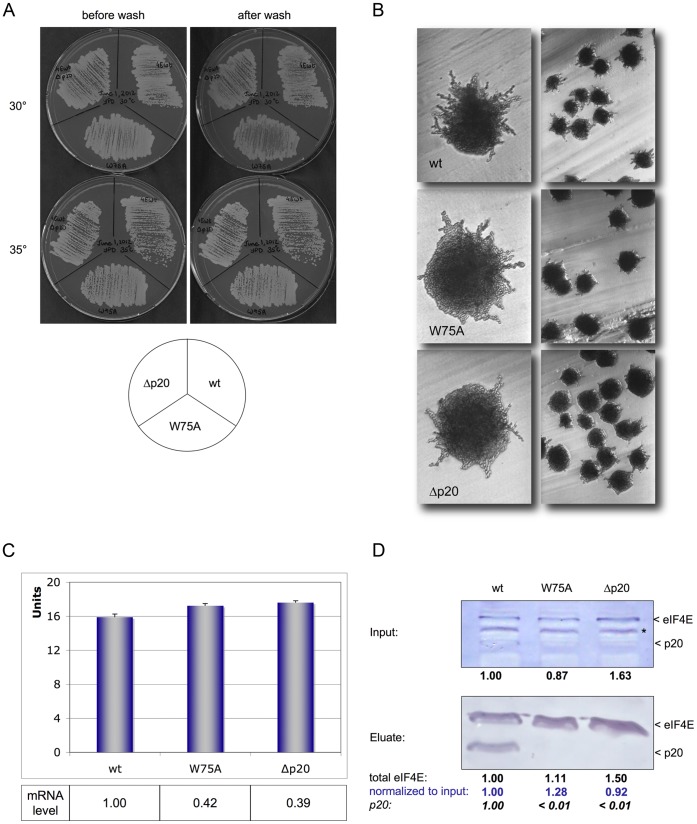
Figure 3. eIF4E mutants W75A (affecting p20 interaction) or a knockout of p20 do not loose adhesion and pseudohyphenation.
(A) Adhesion of haploid eIF4E mutants W75A or Δp20 as compared to eIF4E wt. Plates were incubated at 30° or 35°C for 2 days, then washed under a gentle stream of water. (B) Pseudohyphenation of diploid eIF4E W75A or Δp20 in comparison to eIF4E wt. Cells were incubated on SLAD50 plates at 30°C for 2 days; shown is a 200× or 40× magnification of cells. (C) ß-Galactosidase activity expressed from Flo11-LacZ in haploid eIF4E wt and mutants W75A and Δp20. Expression levels were normalized to LacZ mRNA content which was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (D) Western Blots of eIF4E wt, W75A or Δp20. Top panel: Blot of extract used for binding to m7GDP-Agarose (1/20 volume of input, 50 µg total protein each lane); lower panel: Blot of total eIF4E bound to m7GDP-Agarose (1 mg input), additional decoration with polyclonal antibody against p20. Intensity of eIF4E signals was analysed by ImageJ. Protein inputs for the upper blot were normalized with the help of a polyclonal antibody against carboxypeptidase Y (Prc1p; not shown), numbers represent the relative eIF4E content as compared to wt protein. Eluted eIF4E bands were furthermore normalized against total eIF4E input as determined for each extract (in blue). Asterix indicates an unspecific band. Signal strength of p20 is indicated in cursive numbers.