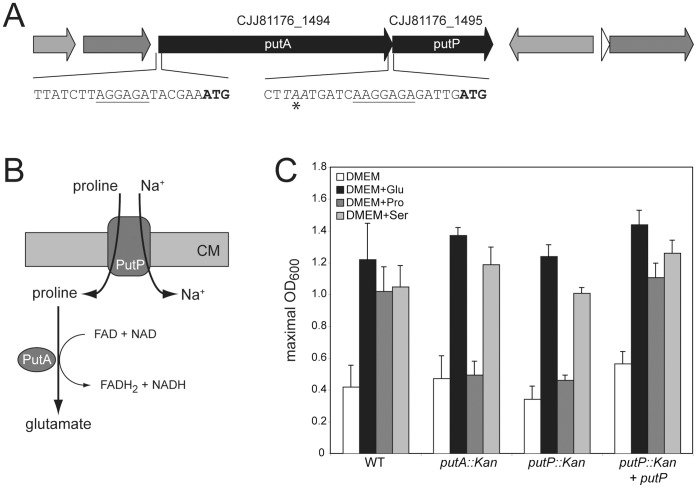
Figure 5. Proline metabolism in C. jejuni 81-176.
(A) The gene locus of C. jejuni 81-176 encoding the proline permease PutP and the bifunctional proline dehydrogenase PutA is shown. The start codons (bold) and Shine-Dalgarno-sequences (underlined) of putA and putP as well as the intergenic region are indicated below the gene region. (B) Schematic model of the proline uptake system in C. jejuni. After proline is being co-imported with sodium ions by the permease PutP into C. jejuni, the cytoplasmic, bifunctional proline dehydrogenase PutA converts proline into glutamate. (C) The ability of C. jejuni 81-176 wild-type strain, its isogenic putA and putP mutants as well as the complemented putP mutant strains to utilize proline as a growth substrate. Values are the mean ± SD of at least three determinations of maximal reached optical density by C. jejuni 81-176 and its mutant derivates in liquid culture. The growth of C. jejuni in DMEM supplemented with 20 mM glutamate, proline or serine occurred over 24 hours at 37°C in 10% CO2.