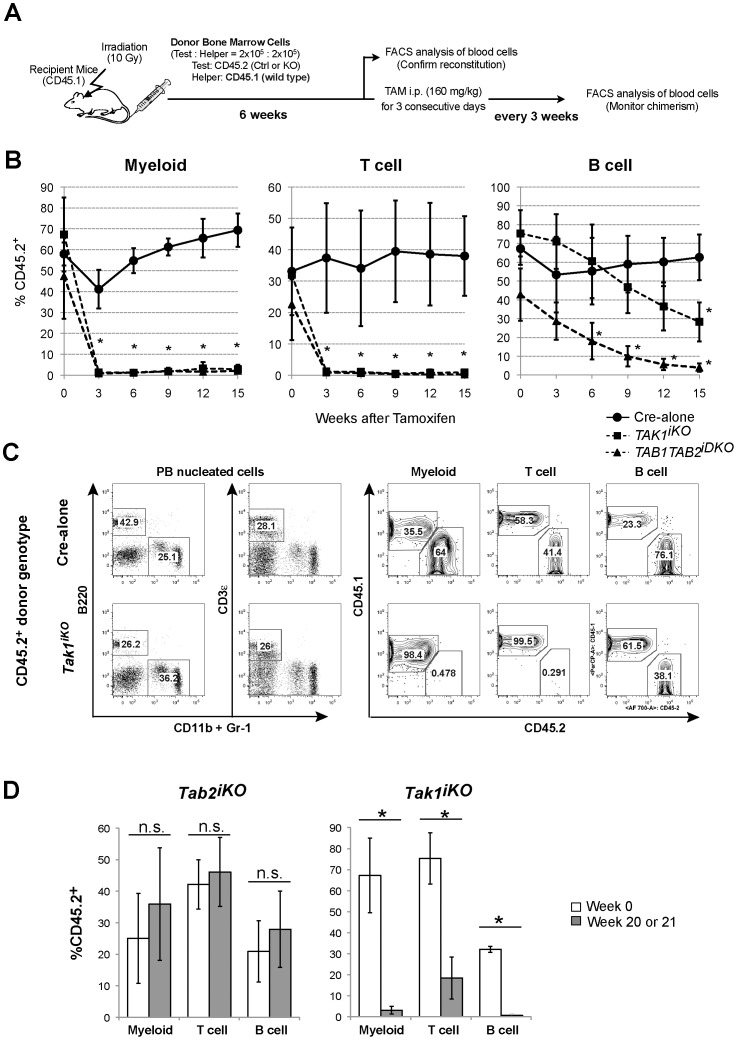
Figure 2. Competitive reconstitution assay.
(A) Schematic representation of competitive transplantation. 2×105 BMN cells from Cre-alone, Tak1iKO or Tab1Tab2iDKO mice (CD45.2+) were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients (CD45.1) together with 2×105 competitor wild type BMN cells (CD45.1+). At six weeks post-transplantation (designated as Week 0), the chimerism of myeloid, T and B cell populations in the recipients’ peripheral blood (PB) was analyzed, then the recipients were i.p. injected with tamoxifen at 160 mg/kg body weight for three consecutive days. (B) The chimerism of PB cell populations was monitored every three weeks, and shown as mean ± S.D. (*p<0.05). [Cre-alone (solid line, circles, n = 3), Tak1iKO (dashed line, squares, n = 3) or Tab1Tab2iDKO (dashed line, triangles, n = 4)]. (C) Representative flow cytometry data of blood cell chimerism. PB cells were collected 15 weeks after tamoxifen injection. Myeloid cells (CD11b+ or Gr-1+), B cells (B220+) and T cells (CD3ε+) in PB mononuclear cells were analyzed for the expression of CD45.1 or CD45.2. (D) Competitive reconstitution assay for Tab2iKO and Tak1iKO mice. Donor-derived chimerism of PBs was analyzed. The percentage of Tab2iKO or Tak1iKO PB myeloid, T and B cells (CD45.2+) in total PB myeloid, T and B cells (CD45.1+ and CD45.2+) before (Week 0, open bars) and 20 weeks or 21 weeks, respectively, after tamoxifen injection is shown (gray bars). Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (*p<0.05, n.s. not significant, n = 3).