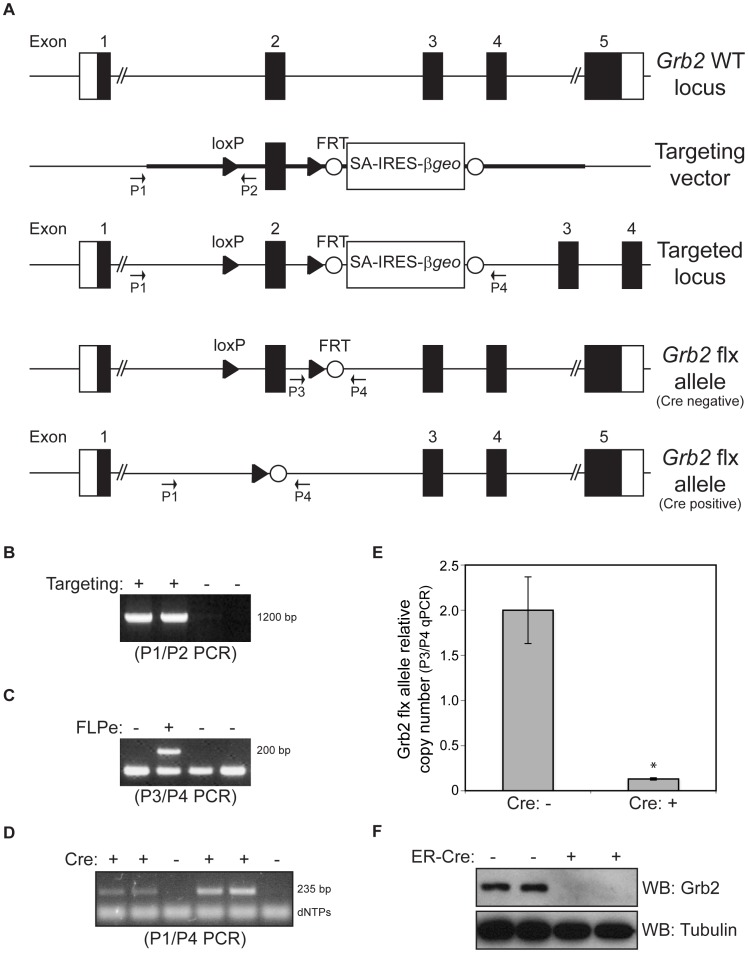
Figure 2. Conditional inactivation of the Grb2 gene in mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the Grb2 locus targeting strategy and the resulting conditional Grb2flx allele. LoxP sites are represented with white triangles and FRT sites with white circles. Genotyping primers P1 to P4 are shown. (B) Example of 2 positive ES clones targeted at the Grb2 locus, as judged from a positive P1/P2 PCR product of 1200 bp. (C) Example of a successful FLPe-mediated excision of the SA-IRES-βgeo-pA cassette to generate the Grb2flx allele, as judged from a positive P3/P4 PCR product of 200 bp. (D) PCR analysis of Cre-mediated excision of the Grb2flx allele in mouse glomeruli. A 235 bp P1/P4 PCR product confirms excision at the locus and correlates with the presence of Cre recombinase. (E) qPCR analysis of Cre-mediated excision of the Grb2flx allele in FACS-sorted podocytes from Podocin-Cre; Nephrin-CFP; Grb2flx/flx (mutant, Cre+, n = 2) or Nephrin-CFP; Grb2flx/flx (control, Cre-, n = 3) mice. Amplification levels of a P3/P4 PCR product were normalized to B-actin and used to calculate relative copy numbers of the non-excised Grb2 flx allele (Cre-: 2.00±0.37 and Cre+: 0.13±0.01). Star represents p-value of 3.8E-05. (F) Western blot showing 2 examples of ROSA-CreER-mediated inactivation of the Grb2flx allele in MEFs, resulting in the absence of the Grb2 protein product. Positive Cre (+) indicates treatment with OHT to activate the expression of the transgene.