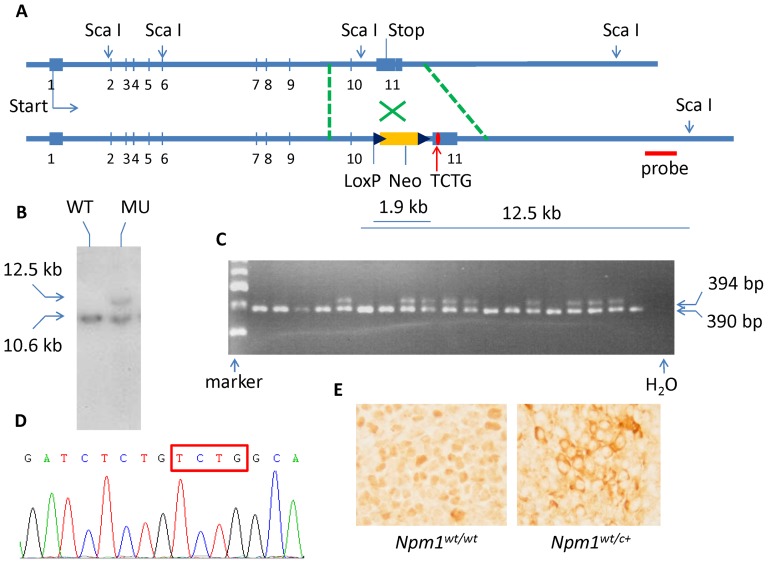
Figure 1. Generation of Npm1wt/c+ mutation knock-in mice.
(A) Mouse knock-in mutation construct map with the sites of ScaI restriction sites and fragment length. The loxP-neo-loxP cassette was removed before injection into foster mothers. (B) The knock-in was confirmed by Southern blot using a probe (as shown in panel A) which hybridized DNA digested with ScaI. (C) The mutant mice were confirmed by genotyping of the tail vein DNA. The upper band (394 bp) and lower band (390 bp) represented mutant and wild-type PCR products, respectively. Please note no homozygous mutant mice were born. (D) The mutant Npm1 sequence was confirmed in DNA level by direct sequencing of the individual TA clones from PCR products of mutant mice. The box indicates the mutated nucleotides. (E) The immunohistochemistry of Npm1 protein in mononuclear cells obtained from mouse spleen cells. The wild-type protein is located in the nuclei, whereas the mutated Npm1 shows aberrant cytoplasmic localization.