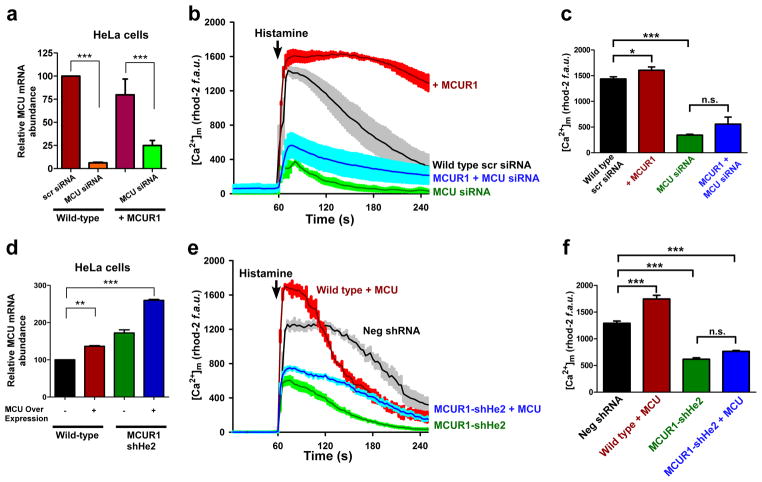
Figure 4. MCUR1 is essential for MCU-dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake.
(a) qRT-PCR of MCU mRNA from wild type and stable MCUR1 over-expressing HeLa cells that were transiently transfected with scrambled siRNA or siRNA against MCU. ***P < 0.001 (mean ± s.e.m). (b) [Ca2+]m responses to histamine (100 μM) in HeLa cells stably over-expressing MCUR1 and in cells transiently transfected with scrambled siRNA or MCU siRNA, and in stable MCUR1 over-expressing HeLa cells transfected with MCU siRNA. After 48 hr of siRNA transfection, cells were loaded with rhod-2 and [Ca2+]m responses were visualized by confocal microscopy. (solid lines are mean; shaded regions are ± s.e.m.; n= 3). (c) Quantification of peak rhod-2 fluorescence following histamine stimulation. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (mean ± s.e.m; n=3). (d) qRT-PCR of MCU mRNA from wild type and MCUR1 knockdown HeLa cells that were transiently transfected with MCU cDNA. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (mean ± s.e.m.; n=3). (e) [Ca2+]m responses to histamine (100μM) in wild-type and MCUR1 (shHe2) knockdown HeLa cells over-expressing MCU. Negative shRNA and MCUR1-shHe2 cells were used as controls. (solid lines are mean; shaded regions are ± s.e.m.; n= 3). (f) Quantification of peak rhod-2 fluorescence following histamine stimulation. ***P < 0.001 (mean ± s.e.m; n=3).