Abstract
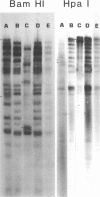
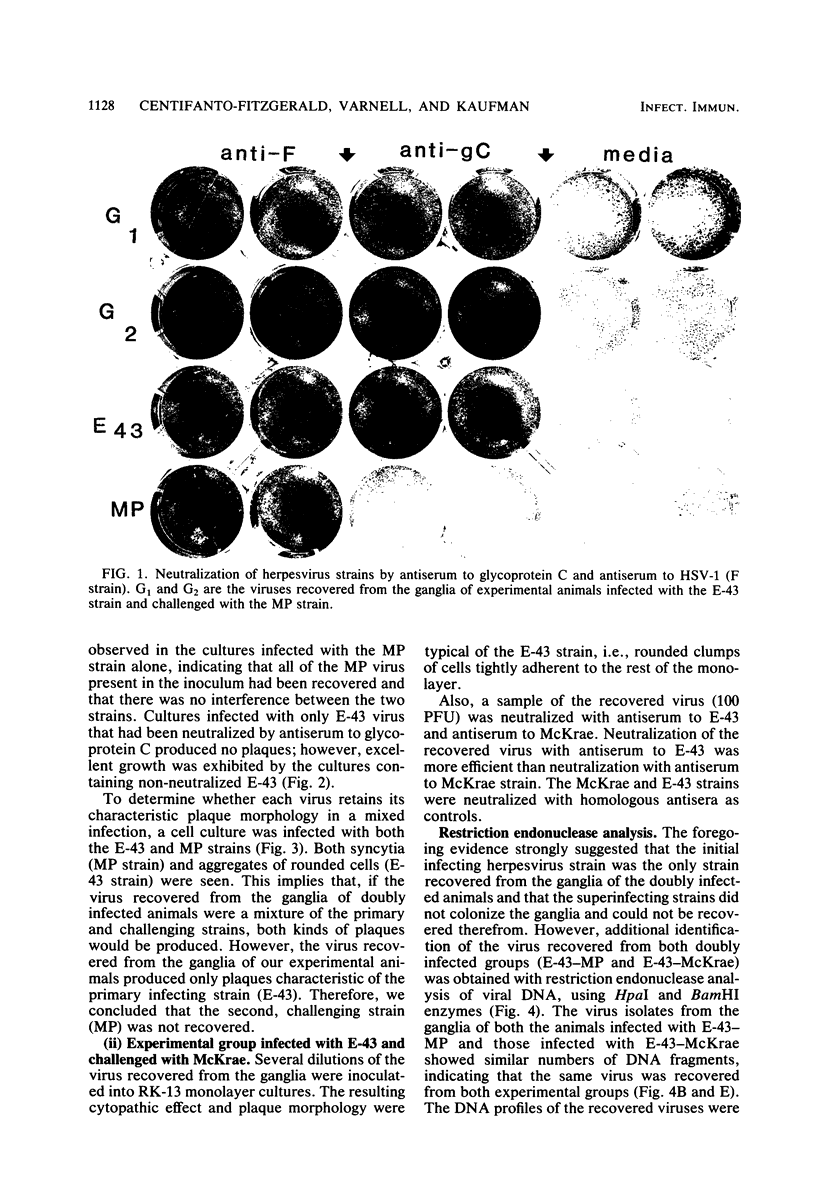
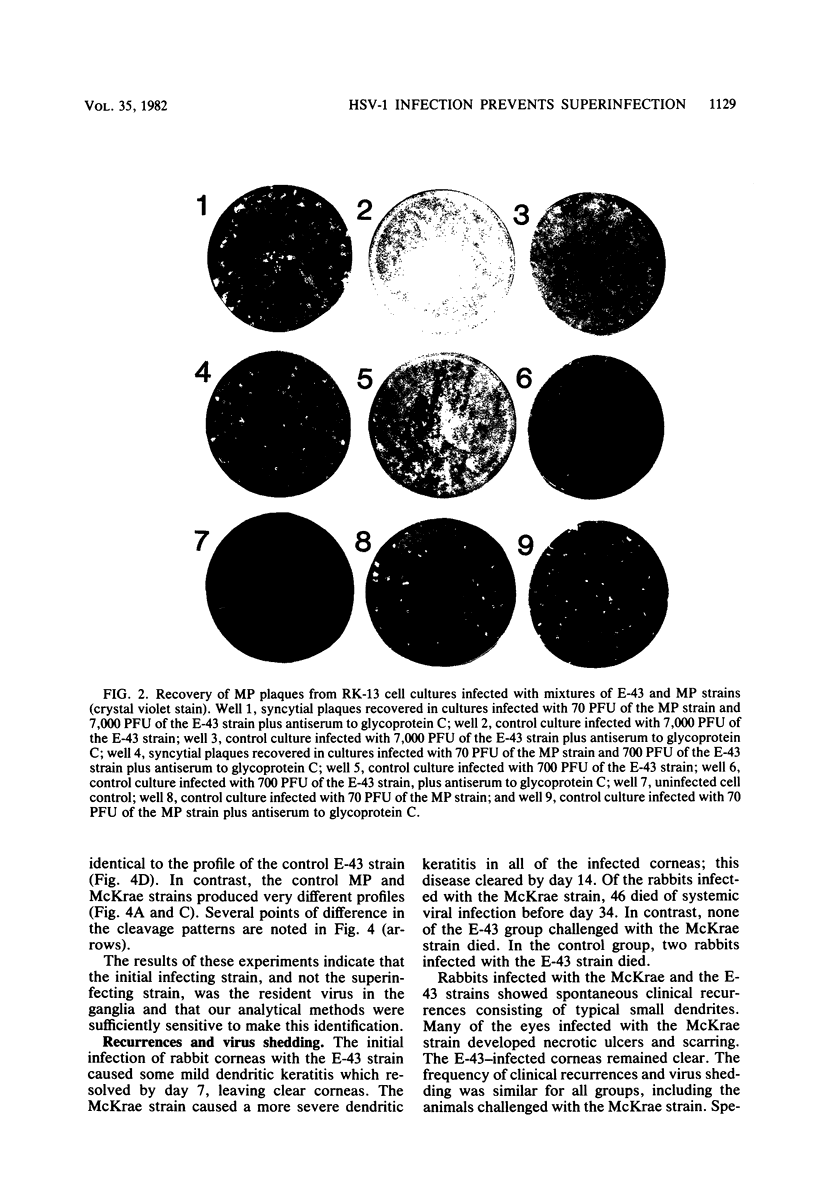
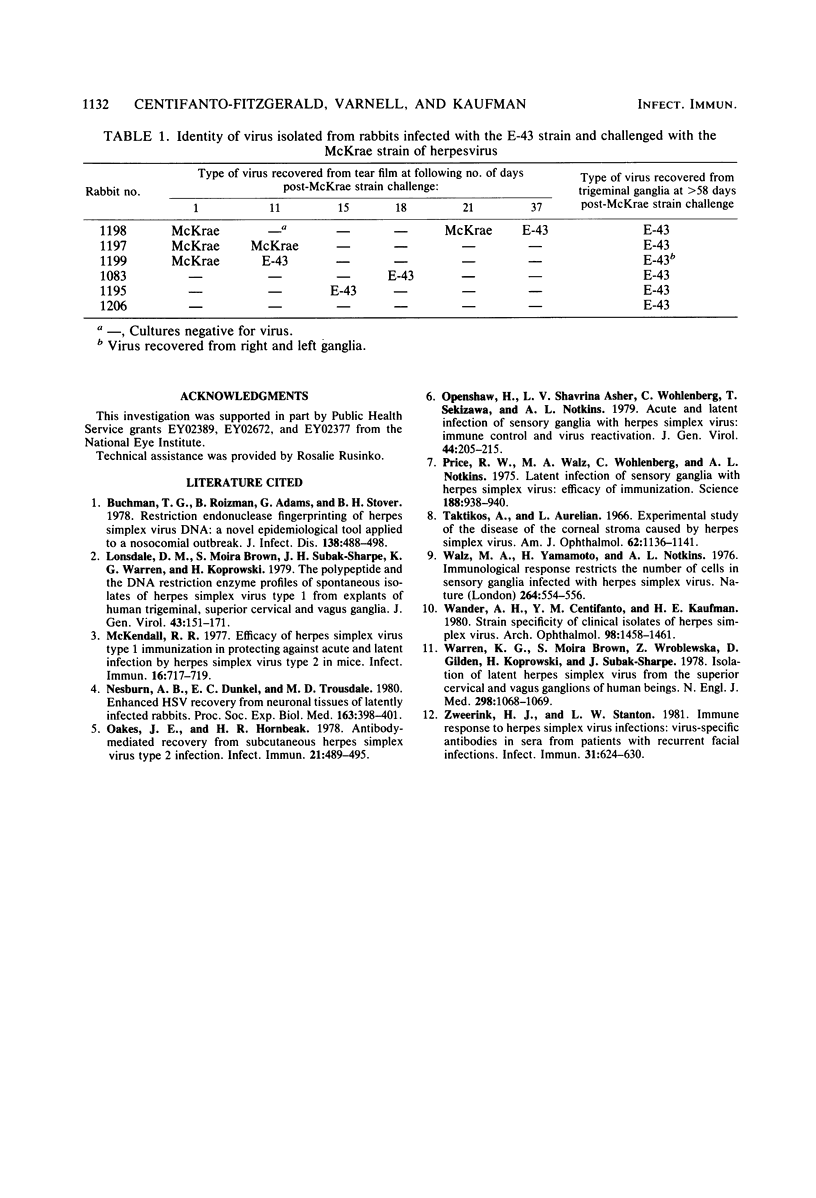
The ganglia of rabbits infected with a relatively benign strain of herpesvirus (E-43) and challenged with either of two virulent neurotrophic strains (MP or McKrae) were found to be colonized only by the initial benign infecting strain. Primary infection with the E-43 strain resulted in milder disease when the animals were infected with MP or McKrae strains and also prevented colonization of the ganglion by these strains. Neutralization with anti-glycoprotein C, plaque morphology, cytopathic effects, reconstruction experiments, and restriction endonuclease analysis indicated that the virus recovered from the ganglion was the initial infecting E-43 strain; no traces of the challenging MP and McKrae strains were found. The challenging McKrae strain was shed for several weeks in a few animals, but the virus isolated from the trigeminal ganglia of these animals was the primary infecting E-43 strain. These results suggest that initial infection with a relatively benign strain of herpesvirus may prevent superinfection of the ganglion (but not necessarily the end organ) by highly virulent herpes simplex virus strains and could have significant implications in the consideration of immunization against this disease in humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Adams G., Stover B. H. Restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of herpes simplex virus DNA: a novel epidemiological tool applied to a nosocomial outbreak. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):488–498. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R. Efficacy of herpes simplex virus type 1 immunization in protecting against acute and latent infection by herpes simplex virus type 2 in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):717–719. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.717-719.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesburn A. B., Dunkel E. D., Trousdale M. D. Enhanced HSV recovery from neuronal tissues of latently infected rabbit. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Mar;163(3):398–401. doi: 10.3181/00379727-163-40785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H. Antibody-mediated recovery from subcutaneous herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):489–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.489-495.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Openshaw H., Asher L. V., Wohlenberg C., Sekizawa T., Notkins A. L. Acute and latent infection of sensory ganglia with herpes simplex virus: immune control and virus reactivation. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):205–215. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Walz M. A., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L. Latent infection of sensory ganglia with herpes simplex virus: efficacy of immunization. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):938–940. doi: 10.1126/science.166432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taktikos A., Aurelian L. Experimental study of the disease of the corneal stroma caused by herpes simplex virus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966 Dec;62(6):1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(66)92565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. A., Yamamoto H., Notkins A. L. Immunological response restricts number of cells in sensory ganglia infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):554–556. doi: 10.1038/264554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wander A. H., Centifanto Y. M., Kaufman H. E. Strain specificity of clinical isolates of herpes simplex virus. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980 Aug;98(8):1458–1461. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1980.01020040310020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Brown S. M., Wroblewska Z., Gilden D., Koprowski H., Subak-Sharpe J. Isolation of latent herpes simplex virus from the superior cervical and vagus ganglions of human beings. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 11;298(19):1068–1069. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805112981907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Koprowski H., Lonsdale D. M., Brown S. M., Subak-Sharpe J. H. The polypeptide and the DNA restriction enzyme profiles of spontaneous isolates of herpes simplex virus type 1 from explants of human trigeminal, superior cervical and vagus ganglia. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):151–171. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Stanton L. W. Immune response to herpes simplex virus infections: virus-specific antibodies in sera from patients with recurrent facial infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):624–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.624-630.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]