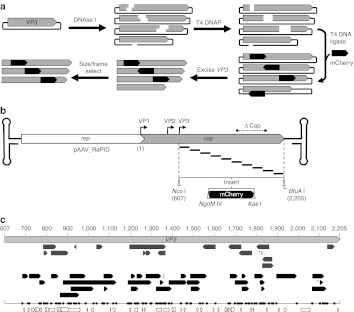
Figure 1.
Construction of pAAV2_RaPID, a modular, enriched random domain insertion library. (a) The random insertion library was constructed by brief DNase I treatment of a plasmid containing the cap gene, resulting in a library of randomly linearized vectors. After blunting by T4 DNA polymerase, a modular linker (mCherry ORF) flanked by unique RE sites, NgoM IV and Kas I, encoding small amino acids alanine-glycine and glycine-alanine respectively, was ligated blunt-wise into the library. The resulting cap-insert hybrids were size selected by excision and purification using agarose gel electrophoresis, resulting in a library of capsid genes with a randomly inserted linker. These genes were then enriched for in-frame variants using a pInSALect derivative.31 The enriched gene pool was cloned into the VP3 portion (between Nco I and BfuA I sites) of an AAV2 expression vector, yielding the pAAV2_RaPID library. (b) A scaled diagram of the pAAV2_RaPID library illustrates an array of random deletions/duplications at insertion sites of mCherry–shown below with flanking RE sites NgoM IV and Kas I–throughout the VP3 ORF. The hairpin loops represent the ITRs (not drawn to scale) and ΔCap ind icates the region of cap deleted from the vector into which the library genes were cloned. Start codons of capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 are indicated by bent arrows. Nucleotide numbering used in this study is shown, starting with 1 at the adenosine of the VP1 start codon, continuing with 607 at the adenosine of the VP3 start codon (at a Nco I site), and ending with 2205 at the final nucleotide of the TAA stop codon (next to a BfuA I cut site). (c) Scaled representation of insertions found in sequenced clones from the pAAV2_RaPID library, aligned with the VP3 ORF (light gray arrow, nucleotide positions in VP1 numbering). Arrows indicate both the direction of insert and size of deletion for each clone in the library before (upper, dark gray) and after (lower, black arrows) frame selection. *Indicates a duplication. The one-dimensional scatter plot shows the distribution of all crossover sites (upstream and downstream, naive and enriched). Below, structural features of VP3 are illustrated with arrows (sheets) and cylinders (coils). AAV, adeno-associated virus; ITR, inverted terminal repeat; ORF, open-reading frame; RE, restriction endonuclease.