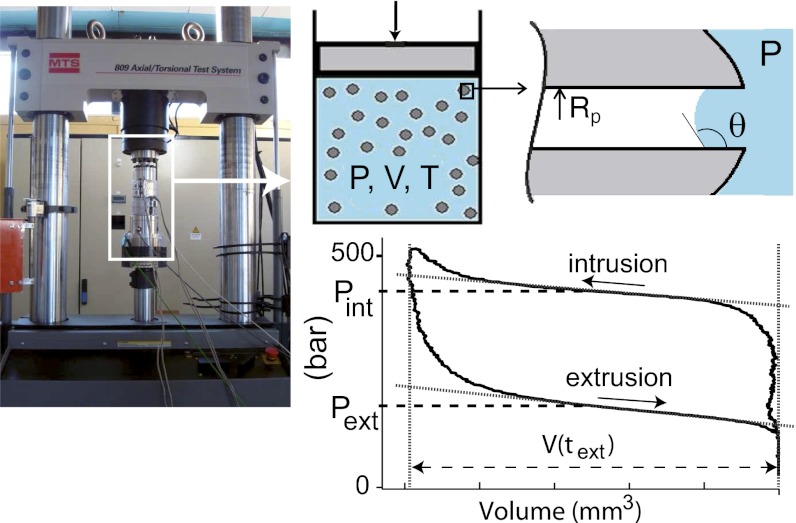
Fig. 1.
Intrusion/extrusion of water in hydrophobic mesoporous silicas. A thermally regulated cell containing water and the material is placed in a traction machine (Left) to measure the pressure–volume isotherms (Lower Right). The volume change is driven at a constant velocity in the range of 0.08–80 mm/s. The intrusion and extrusion pressures, Pint and Pext, respectively, are determined as the average pressure in the corresponding plateaus of the P-V isotherms (24).