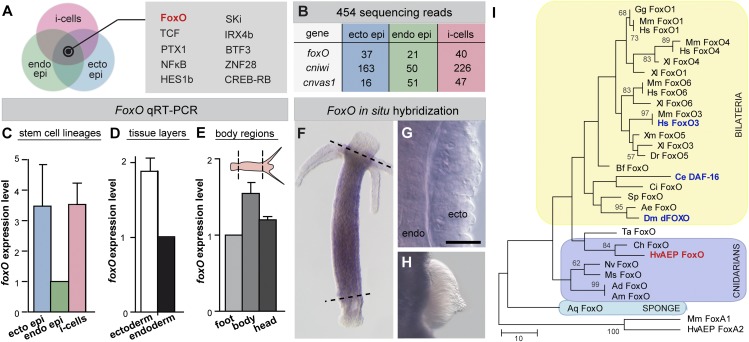
Fig. 2.
foxO is expressed in all three stem cell types in Hydra. (A) Venn diagram of conserved transcription factors being expressed in all three stem cell types according to 454 transcriptome sequencing. (B) Reads from 454 sequencing for foxO, cnvas1, and cniwi. (C–E) qRT-PCR reveals foxO expression in (C) all three stem cell lineages, (D) both tissue layers, and (E) in the body column (n = 2 replicates). Expression in endodermal epithelial cells, endodermal tissue layer, and foot tissue was used as calibrator. (F–H) In situ hybridization shows that foxO is expressed in both tissue layers along the body axis and absent from terminally differentiated cells in head, foot, and (H) gonads. (I) Maximum-parsimony phylogram of the forkhead domain from selected FoxO proteins rooted using Mus musculus FoxA1 and Hydra FoxA2. Numbers at nodes are bootstrap support values calculated by 1,000 replicates of maximum parsimony. Bootstrap values under 50 are not shown. Aa: Aedes aegypti; Ad: Acropora digitifera; Am: Acropora millepora, Aq: Amphimedon queenslandica; Bf: Branchiostoma floridae; Ce: C. elegans; Ch: Clytia hemisphaerica; Ci: Ciona intestinalis; Dm: Drosophila melanogaster; Dr: Danio rerio; Gg: Gallus gallus; Hs: Homo sapiens; HvAEP: H. vulgaris strain AEP; Mm: M. musculus; Ms: Metridium senile; Nv: Nematostella vectensis; Sp: Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; Ta: Trichoplax adhaerens; Xl: Xenopus laevis; and Xm: Xiphophorus maculates. (Scale bar in G: 20 µm.)