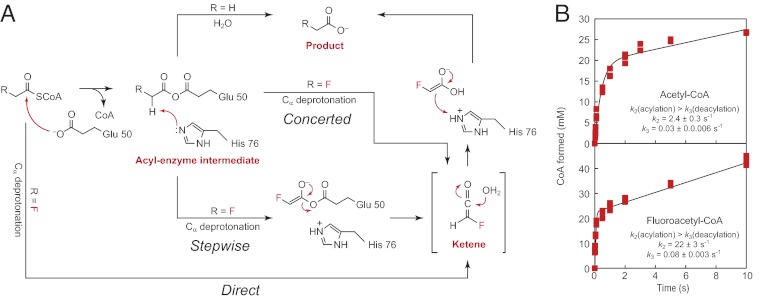
Fig. 3.
A change in catalytic mechanism accounts for FlK’s specificity for fluoroacetyl-CoA. (A) Proposed enzymatic mechanisms for hydrolysis of fluoroacetyl-CoA versus acetyl-CoA. Whereas acetyl-CoA is hydrolyzed through an acyl-enzyme intermediate, fluoroacetyl-CoA could be either directly deprotonated (direct) or deprotonation could occur from a fluoroacetyl-enzyme intermediate in either a stepwise or concerted fashion. (B) Pre-steady-state kinetic traces for hydrolysis of acetyl-CoA (Upper) and fluoroacetyl-CoA (Lower) by FlK-H76A.