Abstract
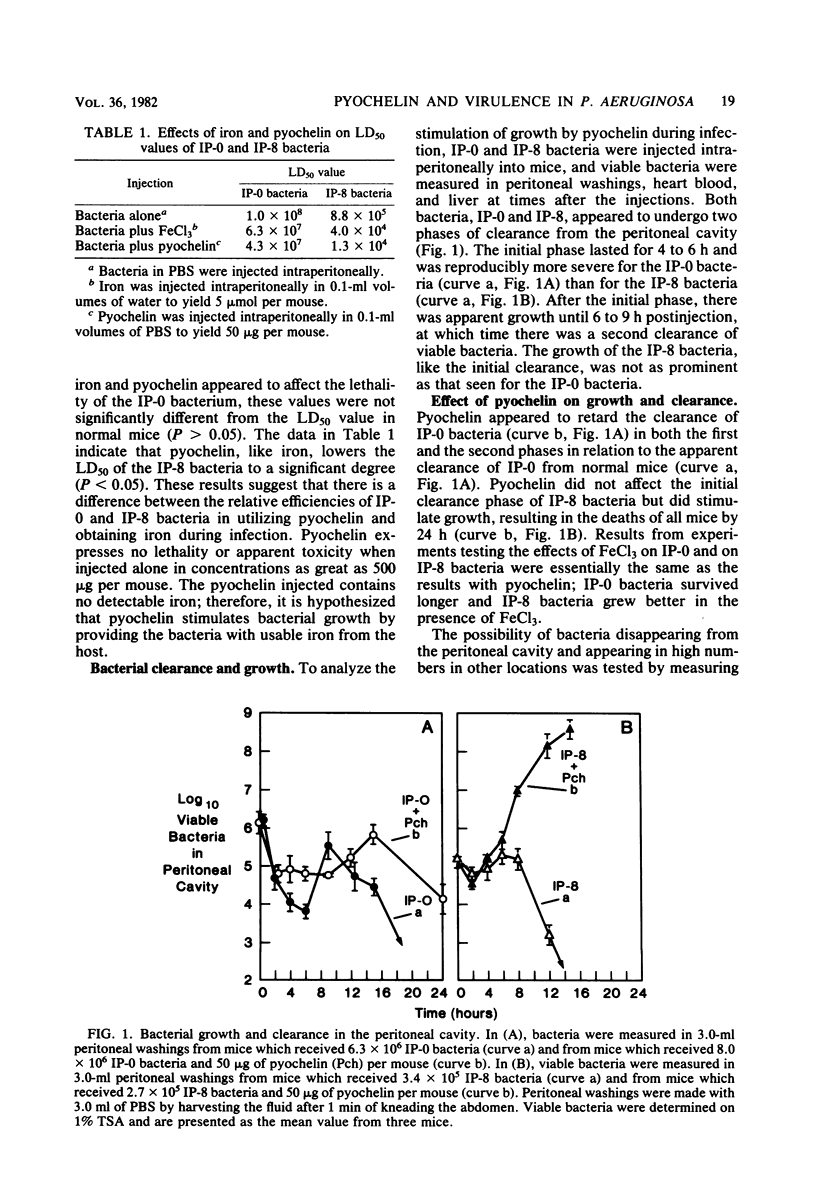
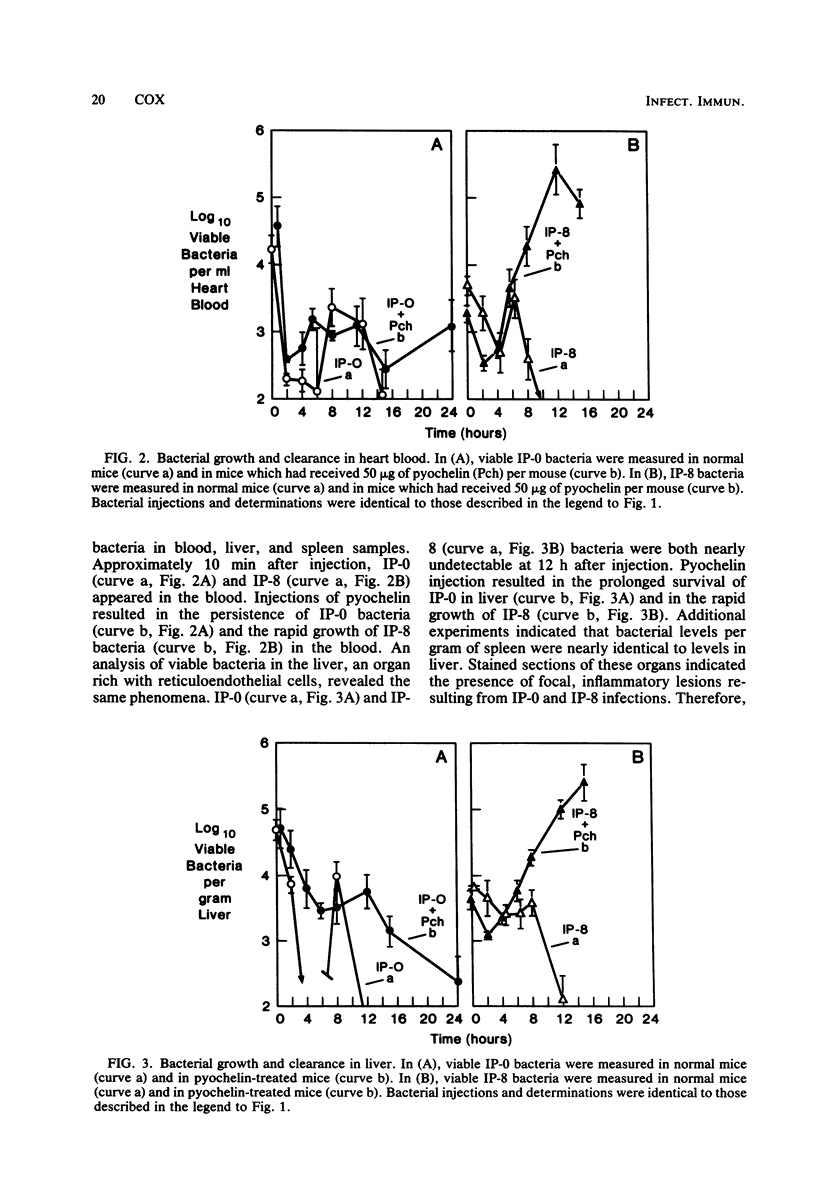
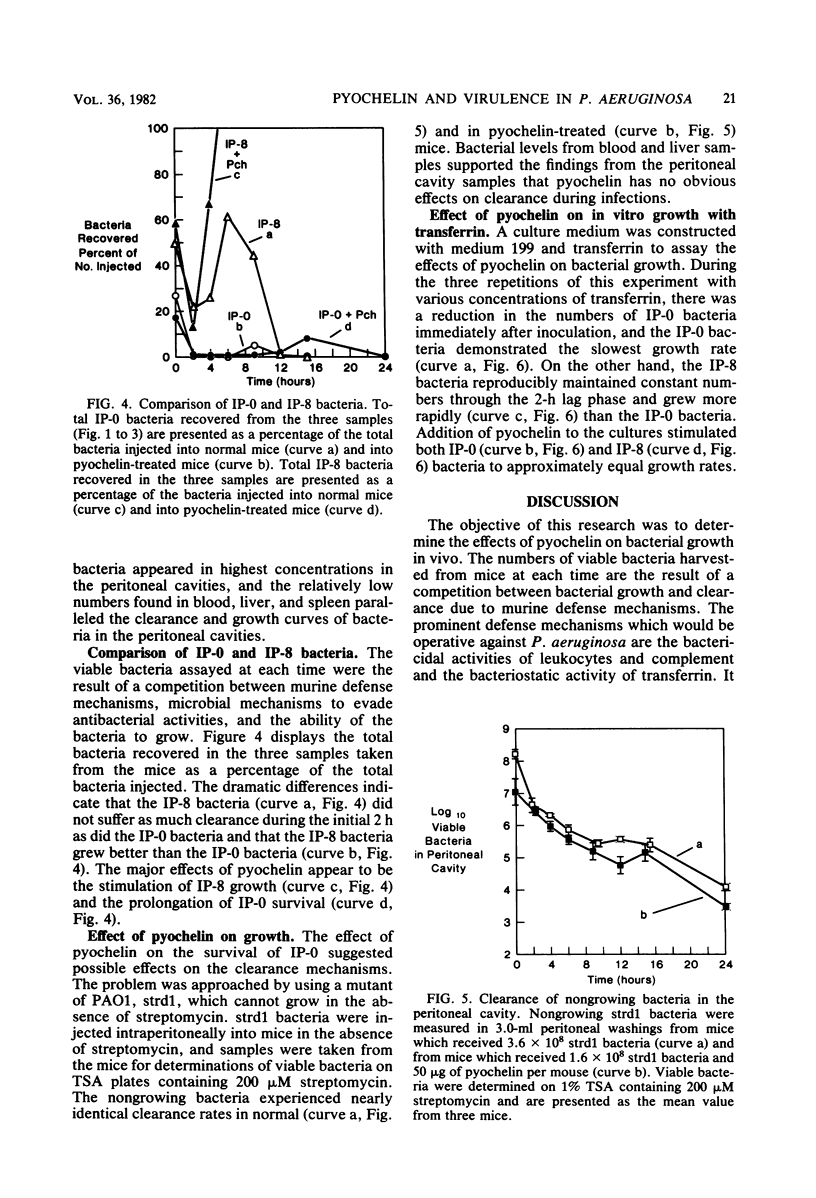
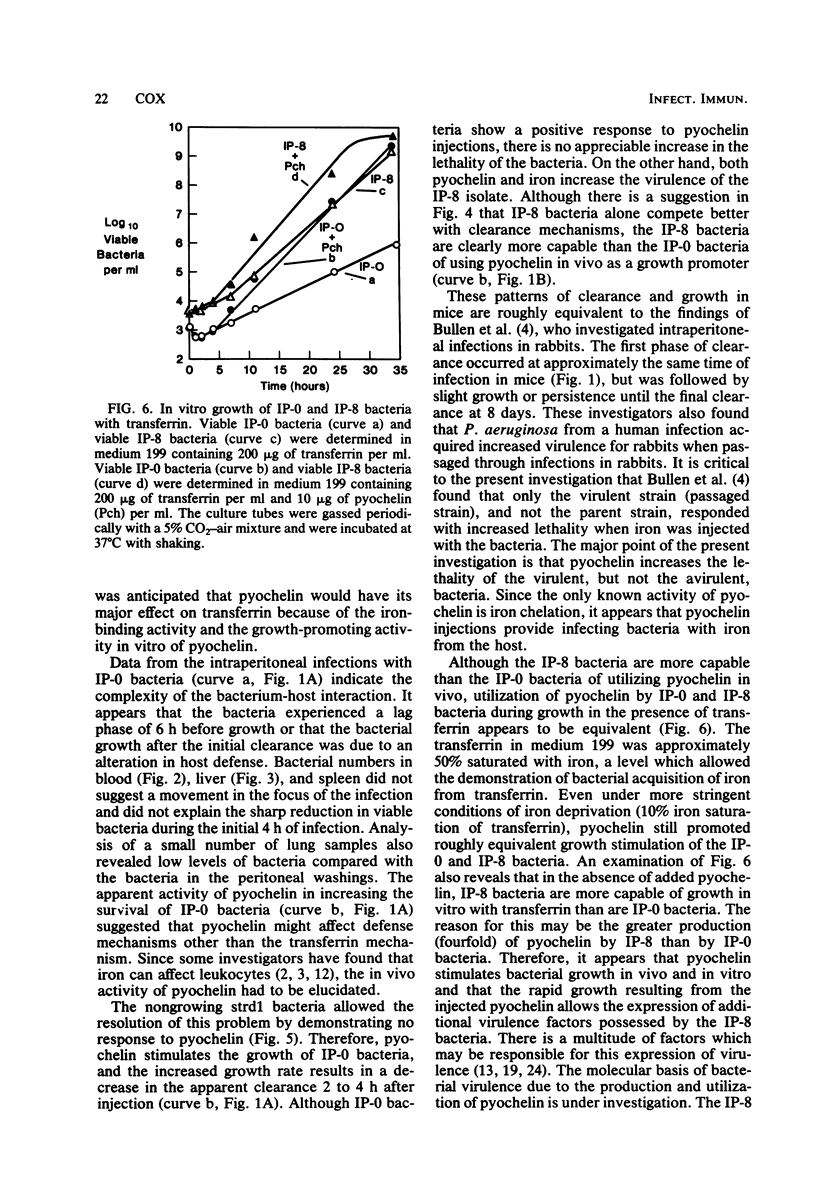
A virulent isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, which had been obtained from eight sequential intraperitoneal infections in mice compromised with iron and methotrexate, expressed greater lethality than the avirulent parent strain when both strains were injected into mice treated with iron. The present study demonstrates that pyochelin, a siderophore produced by P. aeruginosa, also increases the lethality of the virulent bacteria but not of the avirulent bacteria. Analysis of the growth and clearance of both virulent and avirulent strains in mice revealed that pyochelin increased the growth and lethality of virulent bacteria but only increased the survival of the avirulent bacteria. A streptomycin-dependent mutant of strain PAO1 (strd1) was used to demonstrate that pyochelin did not affect the clearance activity of mice. This strongly suggests that the effects of pyochelin in stimulating the persistence of avirulent bacteria and in increasing the lethality of virulent bacteria are due solely to the promotion of bacterial growth. Since the virulent bacteria were equivalent to the avirulent bacteria in utilizing pyochelin during in vitro growth in the presence of transferrin, it appears that the stimulation of growth by pyochelin allows the expression of additional virulence properties by the virulent bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brubaker R. R., Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pestis: Role of Pesticin I and Iron in Experimental Plague. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Wallis S. N., Griffiths E. The effect of antipolymorphonuclear leucocyte serum on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in rabbits. Immunology. 1976 May;30(5):603–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Ward C. G., Wallis S. N. Virulence and the role of iron in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):443–450. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.443-450.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carhart G., Hegeman G. Improved method of selection for mutants of Pseudomonas putida. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1046–1047. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1046-1047.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Graham R. Isolation of an iron-binding compound from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):357–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.357-364.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Iron uptake with ferripyochelin and ferric citrate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):581–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.581-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Passage of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in compromised mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):118–124. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.118-124.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Moore M. L., Cook J. C., Jr Pyochelin: novel structure of an iron-chelating growth promoter for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4256–4260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Yancey R. J. Effect of siderophores on virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):609–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.609-613.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. M., Bullen J. J. The effect of passage and iron on the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):65–68. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone G. P., Walton E. The effect of iron and haematin on the killing of staphylococci by rabbit polymorphs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Oct;52(5):452–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L., Peterson C. M., Grady R. W., Kumbaraci T., Cerami A., Graziano J. H. Effects of iron chelators and iron overload on Salmonella infection. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):63–65. doi: 10.1038/267063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Wasynczuk J., McCabe M. A. Effects of injected iron and siderophores on infections in normal and immune mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):560–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.560-567.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V., MERCER C. B. GROWTH, TOXIGENICITY AND VIRULENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Dec;61:485–491. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Shokrani F. Biological activities of pyochelins: iron-chelating agents of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):878–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.878-890.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A., Pillow J., Khimji P. L. The action of iron on local Klebsiella infection of the skin of the guinea-pig and its relation to the decisive period in primary infective lesions. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Apr;57(2):217–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H. Production of protease and elastase by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):679–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.679-685.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Pathogenesis and immunology of experimental gonococcal infection: role of iron in virulence. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1313–1318. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1313-1318.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Holmes K. K., Finkelstein R. A. Role of iron in disseminated gonococcal infections. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):573–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.573-574.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade A. L., Caroline L. An Iron-binding Component in Human Blood Plasma. Science. 1946 Oct 11;104(2702):340–341. doi: 10.1126/science.104.2702.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake A., Yamamoto M., Morita H. Double effects of an iron drug in induction of mouse plague caused by an attenuated strain. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1974 Aug;27(4):229–239. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.27.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


