Figure 5.
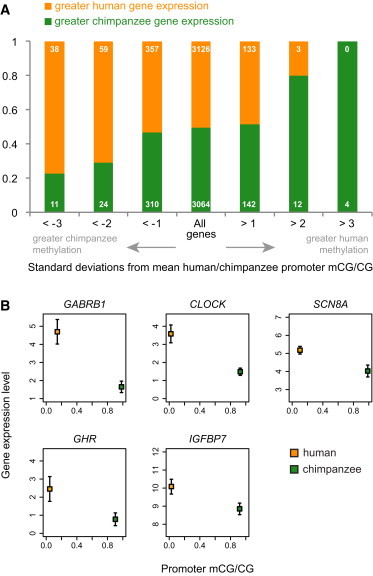
Differences in Promoter Methylation Are Associated with Differences in Gene Expression between the Human and Chimpanzee Prefrontal Cortex
(A) The proportion of genes with higher or lower expression values in humans, as compared to chimpanzees, in the prefrontal cortex. Each bar represents a class of genes and is based on the number of standard deviations from the mean of methylation measures in human versus chimpanzee promoters in the prefrontal cortex.
(B) Selected genes with hypomethylated promoters in humans, hypermethylated promoters in chimpanzees, and significantly higher expression in humans than in chimpanzees. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals of the mean (n = 6). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, beta 1 (GABRB1 [MIM 137190]) is involved in neurotransmission of the CNS. Clock homolog (mouse) (CLOCK [MIM 601851]) encodes a transcription factor essential to the circadian rhythm. SCN8A facilitates the generation of action potentials in neurons and other cells. Growth hormone receptor (GHR [MIM 600946]) is integral to activating insulin-like growth-factor production, leading to growth. IGFBP7 regulates insulin-like growth-factor availability and receptor binding.
