Figure 2.
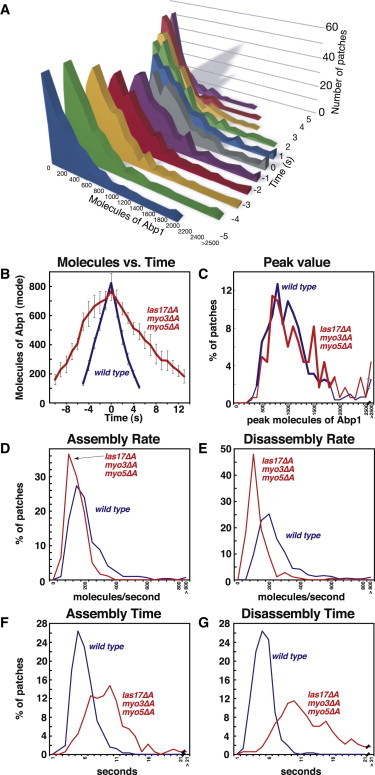
Assembly of Abp1, a marker for actin filaments, in actin patches over time. (A) Data for the absolute number of molecules of the Abp1 in patches over time. At each time point (y axis), the figure shows a histogram of the number of patches (z axis) that contain a certain number of Abp1 molecules (x axis). The data include 323 actin patches from 24 WT cells. (B–G) Analysis of Abp1 assembly in WT (blue) and las17Δacidic myo3Δacidic myo5Δacidic (red) cells. Data are from three segregants of each genotype. (B) Number of molecules of GFP-Abp1 per patch versus time. Plots were generated from data aligned at the maximal (peak) value for each patch. This time point was defined as zero, and the mode of the distribution at each time point was graphed. Error bars are ± one standard error of the mode. (C) Histogram of the peak number of molecules in patches. (D) Histogram of the rate of assembly. (E) Histogram of the rate of disassembly. (F) Histogram of the duration of Abp1 assembly. (G) Histogram of the duration of disassembly. Strain numbers and numbers of patches analyzed were as follows. Abp1-GFP strains: WT, YJC6718-20, N = 99, 114, 110; WASp/las17Δacidic myo3Δacidic myo5Δacidic, YJC7151-3, N = 75, 65, 44. Cse4-GFP: YJC6725-6.
