Figure 6.
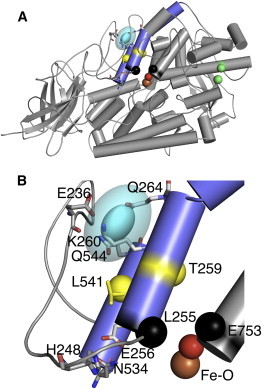
The LOPTC spin placed in the SBL1 structure (PDB:1YGE). (A) The experimental PDS solution for the location of the LOPTC spin is superimposed on the overall structure of SBL1(helices 2 and 11, slate gray). Helix 2 is separated into two portions by P268. The experimental LOPTC spin location (cyan ellipsoid) of radii 1.2, 2.3, and 3.0 Å, corresponding to the 1σ confidence level (distance distributions in one dimension), and an outer ellipsoid with radii twice those as an approximation of the 2σ confidence level. The coordinates of the center of the ellipsoid are 30.4, 62.2, and 12.2 Å. The catalytic Fe-water are colored by atom. The α-carbon atoms of side-chain pairs blocking possible entrances (3,4) into the cavity are show as colored spheres (yellow for T259 and L541, black for L255 and E753, and green for M341 and L480). (B) A portion of Fig. 6A (residues 213–276, 534–546, 750–756, and 840-841 (Fe-water)) is enlarged to provide details of the pocket in which the LOPTC spin resides (same orientation as in panel A). The loop region, composed of amino acids 213–254 (smooth loop) shows only the E236 side chain. Residues closest to the ellipsoid (cyan) are labeled (E236, K260, Q264, and Q544). (Lower region) E256 oxygens (helix 2) form a salt bridge with H248 (loop) and a hydrogen bond with N534 (helix 11). The orientation of SBL1 in this figure is related to that in Fig. 2 by rotations of the viewing direction by ∼40° about x and 30° about z.
