Figure 2.
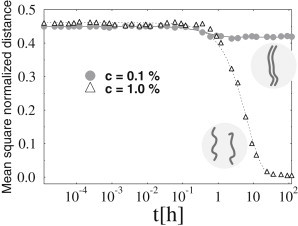
Dynamics of colocalization in a two-polymer system. The normalized polymer mean-squared distance, d2(t), is plotted as function of time t at a fixed binding energy E = 3.4 kT, for the two shown values of the molecule concentration, c, above and below threshold. The polymers are initially positioned at a given distance. At the lower concentration (c = 0.1%, circles), the polymers do not colocalize and attain the average distance of two randomly located polymers. When the concentration is raised to c = 1.0% (triangles), the colocalization transition occurs (see Fig. 1) and the polymers pair off at equilibrium, as shown by d2(t), which eventually collapses to zero. The cases shown concern Model A, but similar behaviors are found with Model B.
