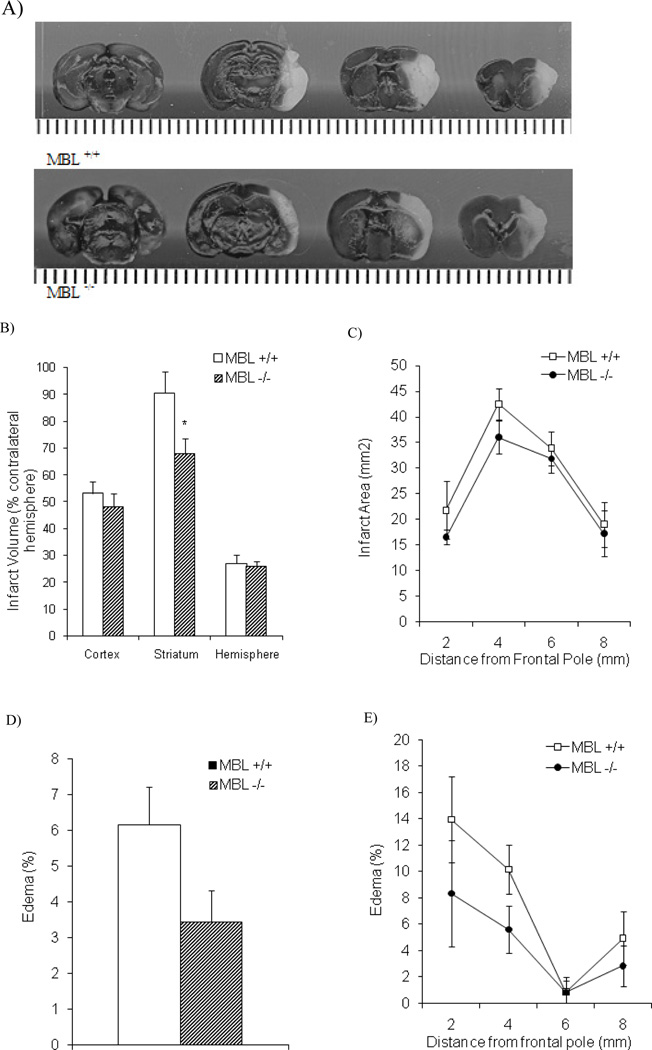
Fig. (5). Cerebral injury in MBL-deficient animals after ischemic stroke and reperfusion.
A) Representative images and of cerebral injury after tMCAO procedure and 24 hours of reperfusion in MBL+/+ (upper panel) and MBL−/− (lower panel). Quantitative analysis of cerebral injury in MBL+/+ and MBL+/+ animals is presented as follows: B) Infarct volume (% contralateral hemisphere) in the cortex, striatum, and total hemisphere (n = 10/MBL+/+, n = 8/c). Analysis of infarct volume illustrate that striatal injury was significantly decreased in MBL−/− versus MBL+/+ animals. C) Total infarct area (mm2) in serial coronal sections in MBL+/+ (n = 10) and MBL−/− (n = 8) groups. Edema present in brain tissue is presented as follows: D) Edema (%) in MBL+/+ (n = 10) and MBL−/− (n = 8) groups. Analysis of hemispheric edema data illustrate that there was no significant reduction in edema between MBL+/+ and MBL−/− (p = 0.07) animals after ischemic stroke and reperfusion. (E) Edema (%) in serial coronal sections in MBL+/+ (n = 10) and MBL−/− (n = 8) groups. Statistical significance versus MBL+/+ was denoted at p < 0.05 (*) (data are mean ± SEM).