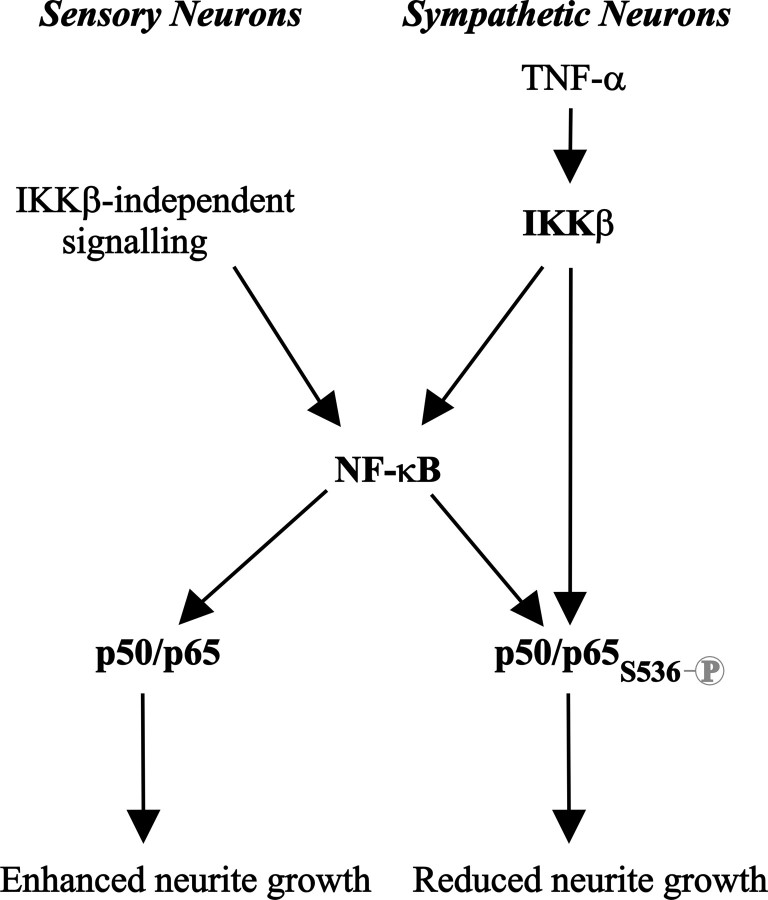
Figure 9.
Schematic model showing the proposed mechanism underlying the opposing effects of NF-κB signaling on neurite growth. In nodose sensory neurons, IKKβ-independent constitutive NF-κB signaling in BDNF-supplemented cultures leads to a transcriptionally active form of p65 that is not phosphorylated on S536 that promotes neurite growth. In SCG sympathetic neurons, IKKβ-dependent enhanced NF-κB signaling after TNFα treatment leads to a transcriptionally active form of p65 that is phosphorylated on S536 that inhibits neurite growth.