Figure 2.
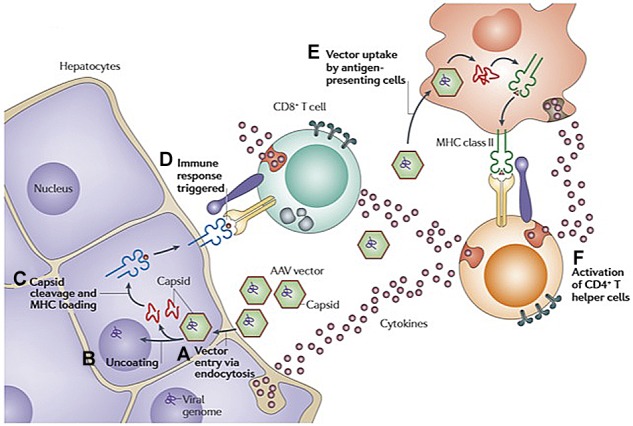
Hypothesis explaining simultaneous rise in liver enzymes and decline in FIX levels at high dose in AAV-FIX trials. (A) AAV enters the cell via receptor-mediated uptake into clathrin-coated endosomes. (B) On endosomal escape, AAV vector is released into the cytosol. Vector genomes are then released from the capsid in a process called uncoating. (C) At least some of the capsid undergoes ubiquitination and proteasomal processing. Capsid-derived peptides are transported to the endoplasmic reticulum and loaded onto MHC class I molecules. The peptide/MHC complexes are displayed on the surface of the transduced cell. (D) MHC class I presentation flags hepatocytes for recognition by capsid-specific CD8+ T cells, resulting in release of cytolytic granules and clearance of the transduced cells. (E) Vector is also taken up by antigen-presenting cells and presented via MHC class II, resulting in (F) activation of CD4+ T helper cells and production of cytokines. Adapted with permission from Figure 3 in Mingozzi and High.61
