Figure 7.
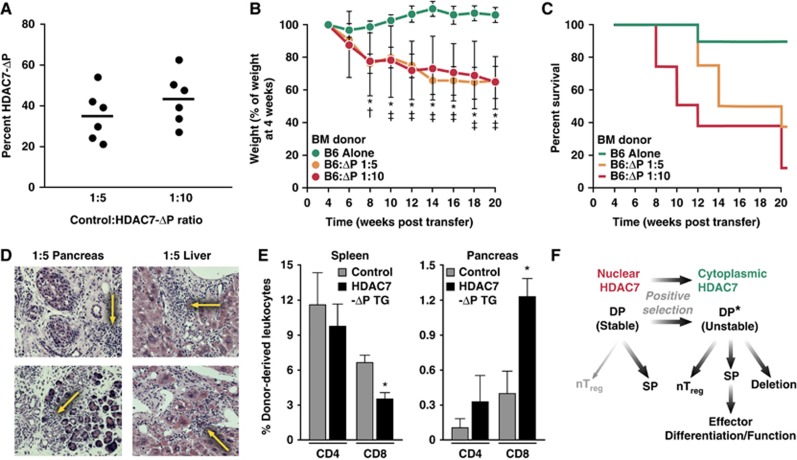
Autoimmunity mediated by HDAC7-ΔP is dominantly transferable in mixed radiation chimeras. (A) Percentage of cells from HDAC7-ΔP TG donors present in circulating T cells in 1:5 and 1:10 WT:HDAC7-ΔP radiation chimeras. Blood was taken 6 weeks after engraftment. (B) Mean weights (in % of weight at 4 weeks post engraftment) of three cohorts, each of eight irradiated BoyJ recipients, engrafted as indicated with WT and HDAC7-ΔP TG bone marrow, from 4 to 20 weeks post engraftment. *P=0.0005–0.0057, two-tailed T-test, WT:HDAC7-ΔP BM at 1:10; †P=0.02, two-tailed T-test, WT:HDAC7-ΔP BM at 1:5. ‡P=7.0 × 10−5–0.013, two-tailed T-test, WT:HDAC7-ΔP BM at 1:5. (C) Percent survival over the same interval of time for the cohorts described in (B). (D) Representative haematoxylin and eosin stained sections of pancreas (left) and liver (right) from two 1:5 WT:HDAC7-ΔP chimeras, showing immune infiltrates and tissue destruction (yellow arrows). (E) Mean percentages of pancreas-infiltrating CD4 and CD8 T cells derived from WT donors, HDAC7-ΔP TG donors, or recipients for five 1:5 WT:HDAC7-ΔP radiation chimeras 10 weeks post engraftment. *P=0.02 for spleen, 0.004 for pancreas, paired two-tailed T-test, for WT versus HDAC7-ΔP populations in the same animal. (F) Diagram depicting model of HDAC7 function in thymic selection, in which nuclear export of HDAC7 destabilizes the signalling network of DP thymocytes during positive selection and enables subsequent developmental programmes.