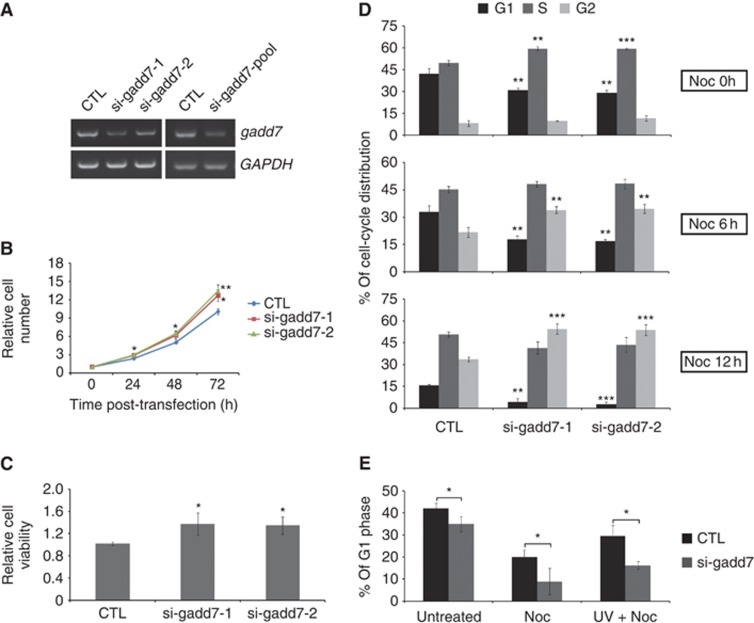
Figure 2.
Defect in the G1/S checkpoint in gadd7-depleted cells. (A) RNAi-mediated knockdown of gadd7 in CHO-K1 cells. CHO-K1 cells were transfected with control siRNA (CTL) or two individual siRNAs targeting gadd7 separately or combined. The expression of gadd7 was detected by semi-quantitative RT–PCR after transfection for 48 h. GAPDH was used as internal reference. (B, C) Knockdown of gadd7 increases cell growth. The relative numbers of CHO-K1 cells transfected with control siRNA or two individual siRNAs against gadd7 were counted daily for 3 days (B), and the relative cell viability was determined by MTT assay after transfection for 72 h (C). Data are represented as mean±s.d. from three independent experiments. *P<0.05 or **P<0.01 compared with control siRNA. (D) Depletion of gadd7 causes a rapid G1/S transition. CHO-K1 cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 48 h were treated with nocodazole (Noc) for 0 h (top panel), 6 h (middle panel) or 12 h (bottom panel). Cell-cycle distribution was measured by PI staining followed by flow cytometry. The percentage of cells in G1, S or G2 phase transfected with control siRNA is defined as control. Data are represented as mean±s.d. from three independent experiments. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (E) gadd7 knockdown results in G1/S checkpoint defect following UV irradiation. CHO-K1 cells transfected with control siRNA or gadd7 siRNA pool for 48 h were treated with nocodazole alone or in combination with UV irradiation just prior to the addition of nocodazole. After 12 h, the distribution of cell cycle was analysed as in (D). Data are represented as mean±s.d. from three independent experiments. *P<0.05.