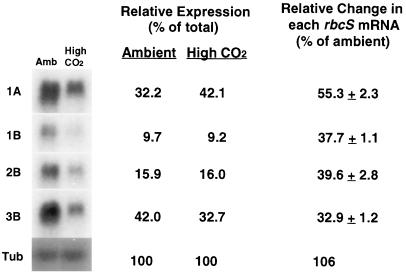
Figure 3.
Effects of long-term growth at elevated CO2 on the relative abundance of rbcS gene members. Ten micrograms of total RNA per lane was used for northern-blot analysis. Gene-specific probes were labeled to similar specific activities (approximately 5 × 107 dpm pmol−1), and equal amounts of radioactivity of each probe were used. Blots were exposed for the same length of time. The relative amounts of individual rbcS mRNA were expressed as a percentage of the sum of hybridizing signals from each of the rbcS members. Relative changes attributable to CO2 treatments were expressed using the ambient values of each rbcS gene as 100%. One of the blots was stripped and hybridized to an internal control gene (α-tubulin [Tub]). Numbers represent means ± sd from two filters each, with RNA samples extracted from two replicate experiments. Leaves were collected at midday.