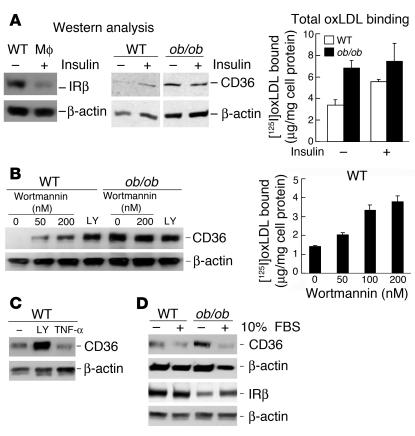
Figure 6.
Defects in insulin signaling in mouse macrophages increase oxLDL binding and CD36 protein expression. (A) Ex vivo effects of chronic high-dose insulin on insulin receptor β-subunit (far left) and CD36 protein expression (middle panels), and oxLDL binding to WT and ob/ob macrophages (far right). Macrophages were incubated with (+) or without (–) insulin (200 nM) for 1 day. Cells were used for oxLDL binding assays or Western analysis with the indicated antibodies. (B) The increase in CD36 protein expression in WT macrophages by the PI3 kinase inhibitor wortmannin is dose dependent. WT or ob/ob macrophages were treated with wortmannin at the indicated concentrations or another inhibitor, LY294002 (LY; 10 μM), for 1 day, followed by protein extraction and Western analysis (left) and by oxLDL binding assays with fucoidan (50 μg/ml) in the binding buffer (right). Inhibition of the insulin receptor effector PI3 kinase results in an increase in oxLDL binding to macrophages. (C) TNF-α has no effect on CD36 protein expression. WT macrophages were treated with LY294002 (LY; 10 μM) or TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 1 day. Total lysates were prepared and Western analysis was performed. (D) CD36 protein expression is reduced by 10% FBS in ob/ob and WT macrophages. Insulin receptors are increased under this condition. All experiments were performed with pooled macrophages isolated from three to six mice of each strain indicated. One experiment representative of three independent experiments is shown.