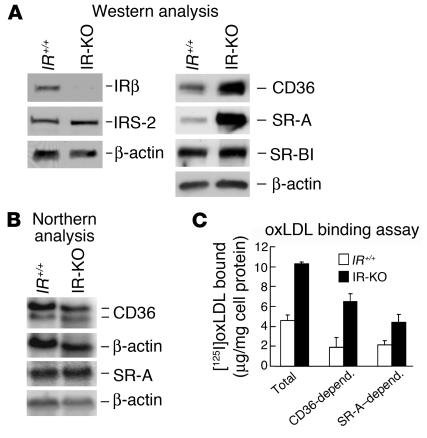
Figure 7.
Lack of insulin receptors in peritoneal macrophages leads to upregulation of CD36 protein expression and oxLDL binding. (A) Western analysis of macrophage IRβ subunit, IRS-2, CD36, SR-A, and SR-BI protein expression in IR knockout (IR-KO) mice rescued with the human IR transgene and in control littermate (IR+/+) mice. Both CD36 and SR-A protein are increased in IR-deficient macrophages. (B) Northern analysis of CD36 and SR-A mRNA levels in macrophages of IR-KO and IR+/+ mice. (C) Assay of oxLDL binding to macrophages from IR-KO and control IR+/+ was carried out with or without the addition of fucoidan (50 μg/ml), mouse anti-CD36 IgA (20 μg/ml), or control IgA (20 μg/ml; not shown) in the binding buffer. CD36-depend. and SR-A–depend., oxLDL binding mediated by CD36 and SR-A, respectively. All experiments were performed with pooled macrophages isolated from three to five mice of each strain. One experiment representative of three independent experiments is shown.