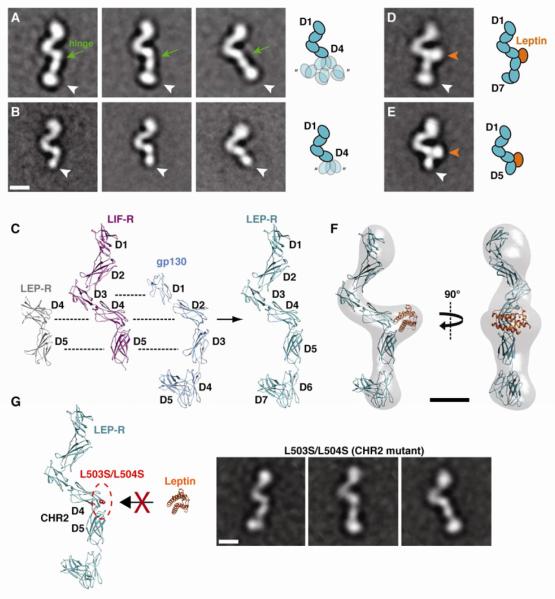
Figure 2. Conformational dynamics of LEP-R in unliganded and liganded states.
A) Representative 2D class averages of unliganded LEP-R[D1-D7] reveal significant flexibility in a hinge between D4 and a rigid D5-D7 module (white arrowheads). B) 2D class averages of unliganded LEP-R[D1-D5] confirm the domain assignments and the variable disposition of D5 (white arrowheads) in regards to D4. C) Comparison of the crystal structures from LEP-R, gp130 and LIF-R extracellular domains and homology model for LEP-R[D1-D7]. D) Representative 2D class average of the binary leptin/LEP-R[D1-D7] complex. The cytokine binds to CHR2 resulting in the stabilization of the rigid D5-D7 module in a single conformation. E) Representative 2D class average the binary leptin/LEP-R[D1-D5] complex. The orange and white arrowheads point to the leptin density and the LEP-R C-terminus, respectively. F) 3D reconstruction of the binary leptin/LEP-R[D1-D7] complex with docked leptin/LEP-R homology model. G) The double mutation L503S/L504S on D4 of Lep-R abolishes leptin binding via epitope II. EM class averages of this mutant after incubation with leptin reveal only monomeric receptor chains with no ligand bound at CHR2 (compare to A and D). All scale bars correspond to 5 nm.