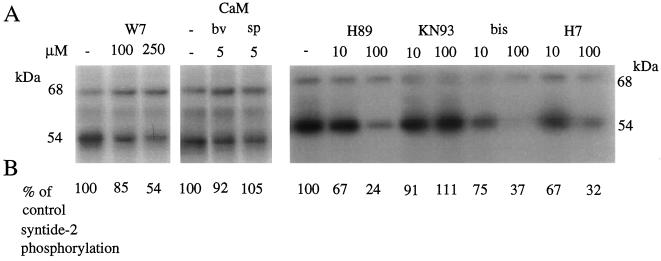
Figure 9.
The effect of protein kinase inhibitors, CaM antagonist W7, and exogenous CaM on autophosphorylation and syntide-2 phosphorylation activities in the barley aleurone. Four protein kinase inhibitors, W7, or CaM (bv, bovine; sp, spinach [Sigma]) were added to autophosphorylation and syntide-2 phosphorylation assays at the indicated concentrations. Aleurone layers were extracted and assays were carried out in the presence of 50 μm CaCl2 as described in Methods. A, Autophosphorylation of the 68- and 54-kD proteins was visualized by autoradiography; B, the effect of protein kinase inhibitors on syntide-2 phosphorylation expressed as a percentage of control (no inhibitor) is shown below the appropriate inhibitor lane on the autoradiograph. The inhibitors used were obtained from Calbiochem: H89, specific for cAMP-dependent protein kinase; KN93, specific for Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase II; bisindolylmaleimide (bis), specific for protein kinase C; and 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H7), a broad-range Ser/Thr kinase inhibitor. The experiments were repeated twice with two replicates each. The largest se for syntide-2 phosphorylation was 12%.