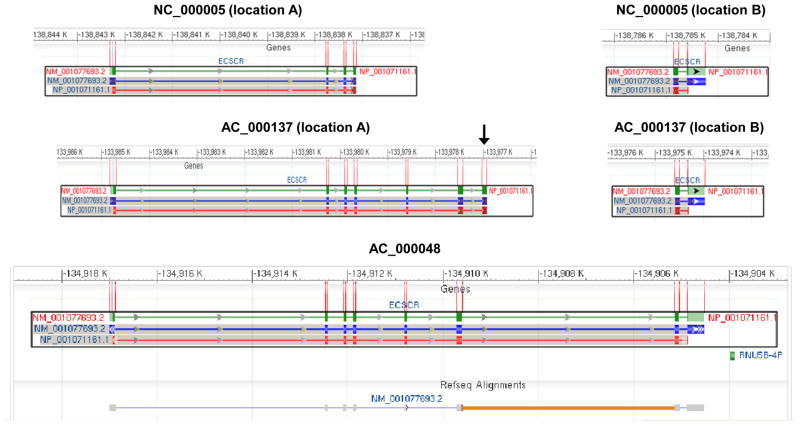
Figure 5. Original gene structure of human ECSCR.
The gene structures shown here are the mapping results on the three assemblies of human chromosome 5 (AC_000137, Homo sapiens chromosome 5, alternate assembly HuRef, whole genome shotgun sequence; AC_000048, Homo sapiens chromosome 5, alternate assembly Hs_Celera, whole genome shotgun sequence; and NC_000005, Homo sapiens chromosome 5, GRCh37.p2 primary reference assembly) that are available in the NCBI databases. Green bars (the first row in each panel) represent the ECSCR gene and blue bars (the second row) show exons. The protein product is in the third row with red bars as translated gene products. Note that the last exon only encodes for two amino acid residues before the stop codon TAA (see ECSCR in Figure 3). On the AC_000048 assembly, a total of eight exons are initially defined. However, the ECSCR gene contains a large, un-sequenced region (thought as a large intron), which is indicated by the orange line. Also, note that the gene is split into two parts (location A and location B) on either AC_000137 or NC_000005 assembly, which together do not cover the entire gene. The black arrow indicates the extra exon identified only on the AC_000137 assembly (location A) but not on the AC_000048 assembly.