Table 4.
Multivariable regression model showing associations of eGFR, serum cystatin C, and UACR with inflammatory markers
| Predictor | Outcome | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β (pg/ml) | IL-1RA (pg/ml) | IL-6 (pg/ml) | TNF-α (pg/ml) | TGF-β (ng/ml) | |||||||||
| eGFR (ml/min per 1.73 m2) (n=3939) | −0.05 (-0.06, -0.04) | P<0.001 | −0.006 (−0.008, −0.003) | P<0.001 | −0.012 (−0.014, −0.01) | P<0.001 | −0.016 (−0.018, −0.015) | P<0.001 | 0.001 (−0.0007, 0.003) | P=0.20 | |||
| Serum cystatin C (mg/L) (n=3927) | 1.4 (1, 1.7) | P<0.001 | 0.19 (0.13, 0.25) | P<0.001 | 0.5 (0.45, 0.55) | P<0.001 | 0.5 (0.46, 0.54) | P<0.001 | 0.02 (−0.03, 0.07) | P=0.43 | |||
| UACR (μg/100 mg) (n=3791)a | 0.009 (−0.003, 0.02) | P=0.15 | 0.0003 (−0.0018, 0.0023) | P=0.78 | 0.006 (0.004, 0.008) | P<0.001 | 0.006 (0.005, 0.008) | P<0.001 | 0.001 (−0.0005, 0.003) | P=0.17 | |||
Values are presented as 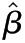 (95% confidence interval). Multivariable linear regression adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, diabetes, hypertension, ACE/ARB use, and lipid-lowering drug use. Outcome variables were log-transformed. P values <0.001 were significant after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Interpretation:
(95% confidence interval). Multivariable linear regression adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, diabetes, hypertension, ACE/ARB use, and lipid-lowering drug use. Outcome variables were log-transformed. P values <0.001 were significant after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Interpretation: 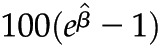 is the percentage increase in the average value of the outcome variable with each unit increase in the predictor variable. As an example, for each unit increase in eGFR, there was a 5% decrease in the average value of IL-1β. eGFR, estimated GFR; UACR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IL-1RA, IL-1 receptor antagonist.
is the percentage increase in the average value of the outcome variable with each unit increase in the predictor variable. As an example, for each unit increase in eGFR, there was a 5% decrease in the average value of IL-1β. eGFR, estimated GFR; UACR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IL-1RA, IL-1 receptor antagonist.
UACR values were converted to μg/100 mg for use in regression analysis.
