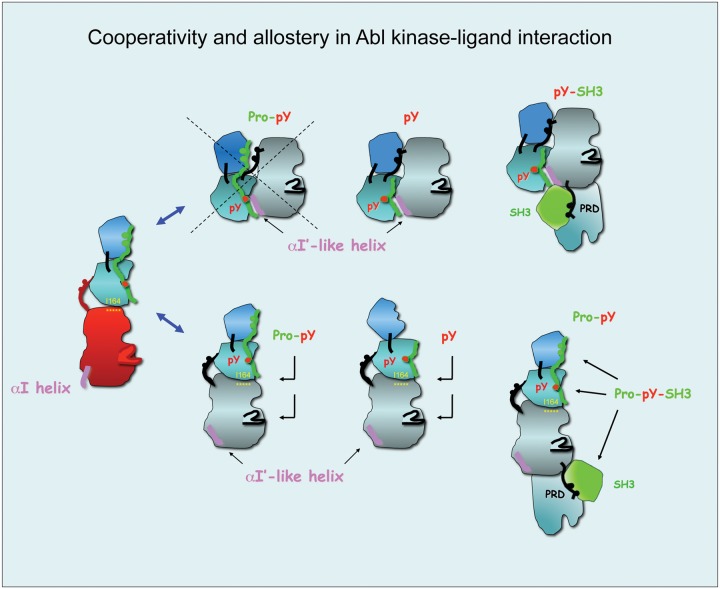
Figure 4.
Cooperativity and allostery in Abl kinase-ligand interactions: candidate binding modes of Abi1 and Crk. Protein modules of Abi1 and Crk have the potential to interact with different Abl kinase conformations and to engage all 3 regulatory domains of Abl. (Top) Potential interactions with the Abl autoinhibitory/closed structure. PXXP-pY peptides cannot engage the Abl SH3-SH2 dual domain in the closed conformation because the Abl SH3 domain interacts tightly with the proline consensus of the SH2–catalytic domain (CD) linker and with the CD interface (left). The SH2 domain, however, might bind phosphopeptides as suggested by modeling data using the autoinhibited Abl structure and Src structure pY527 (not shown). Abi1 pY213 and published Crk pY221/207 data (REF) (middle). In addition, the closed structure might engage the proline-rich region in Abl (PRD) and an SH3 domain in a ligand such as Crk and Abi1 (far right). (Bottom) Potential interactions of ligands with an open/active structure of Abl. PXXP-pY–containing peptides such as Abi1 181-PPSPP-185; pY213 might interact with the Abl SH3-SH2 dual domain (left) and with the SH2 domain (middle). It is not yet known what the effect of such interactions is on the Abl SH2 interface residue I116, which is critical in maintaining Abl kinase activity.45 Moreover, proteins such as Crk or Abi1 might in addition engage the proline-rich linker (PRD) that immediately follows the CD of Abl. In such cases, there is a potential for an additional effect on the CD itself through a possible steric effect.