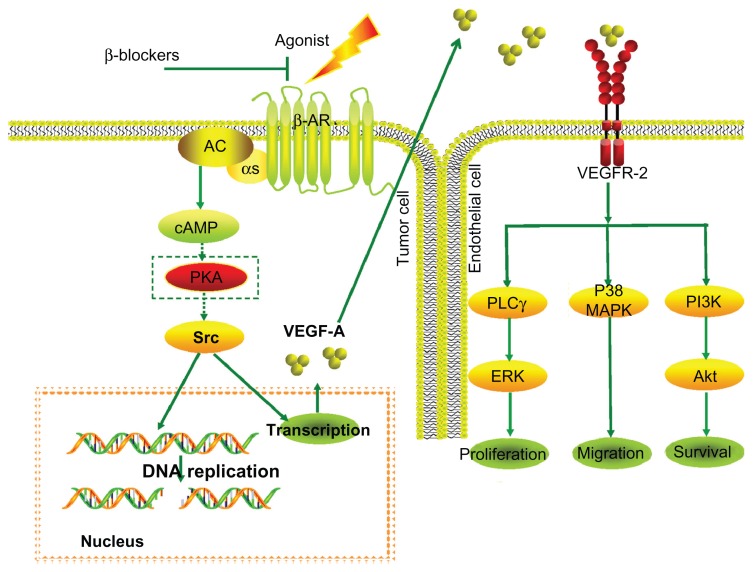
Figure 1.
β-blockers abolish induction of VEGF expression by β-adrenergic agonists, leading to inhibition of angiogenesis.
Notes: The neurotransmitters epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to β-ARs, resulting in Gαs-mediated activation of adenylyl cyclase and subsequent cAMP synthesis. One cAMP effector involves activation of PKA which belongs to a family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases involved in the control of diverse cellular processes. For example, exposure to a chronic stressor promoted production of VEGF. VEGF is a proangiogenic molecule that stimulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration, and promotes endothelial cell survival. Conversely, β-blockers lead to a reduced expression of VEGF and thus to an inhibition of angiogenesis.
Abbreviations: ARs, adrenergic receptors; cAMP, cyclic AMP; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase; PLCγ, phospholipase C-γ; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.