Figure 2.
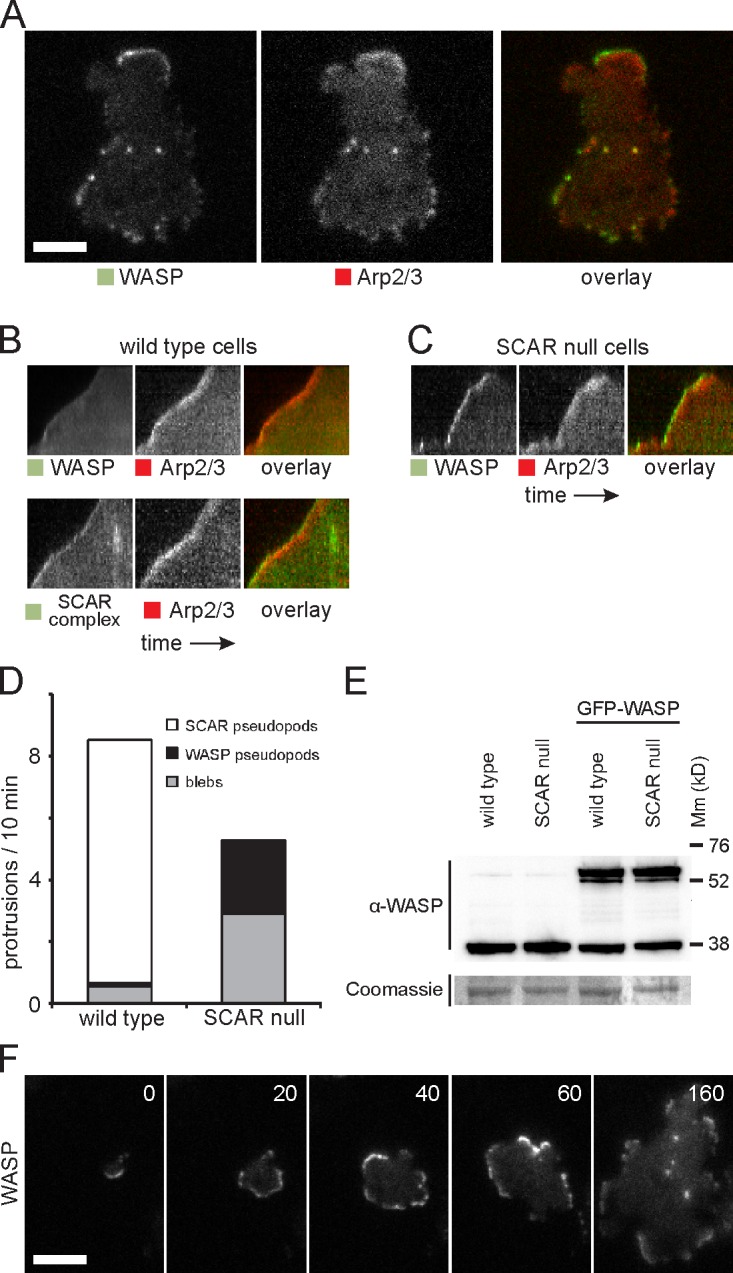
WASP compensates for the loss of SCAR. (A) Colocalization of WASP and Arp2/3 complex in SCAR-null cells. (B) Kymograph showing distribution of GFP-tagged WASP and SCAR complex with RFP-tagged Arp2/3 complex in a wild-type cell protrusion. The protrusion extends upwards, and time is along the horizontal axis. (C) Kymograph of WASP and the Arp2/3 complex in a protrusion of a SCAR-null cell. (D) Quantification of the number of pseudopods with SCAR complex and with WASP and the number of blebs in wild-type and SCAR-null cells. Over 200 pseudopods/blebs were counted in a total of 40 cells that were recorded with time-lapse microscopy for a length of 10 min each. (E) Western blot of whole-cell lysates of the indicated strains with an anti-WASP antibody. After immunodetection, the blot was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. Molecular mass (Mm) size markers are indicated on the right in kilodaltons. (F) TIRF microscopy image of GFP-WASP in a SCAR-null cell that is dropping out of solution and spreading on the glass substratum. Time is indicated in seconds. Bars, 5 µm.
