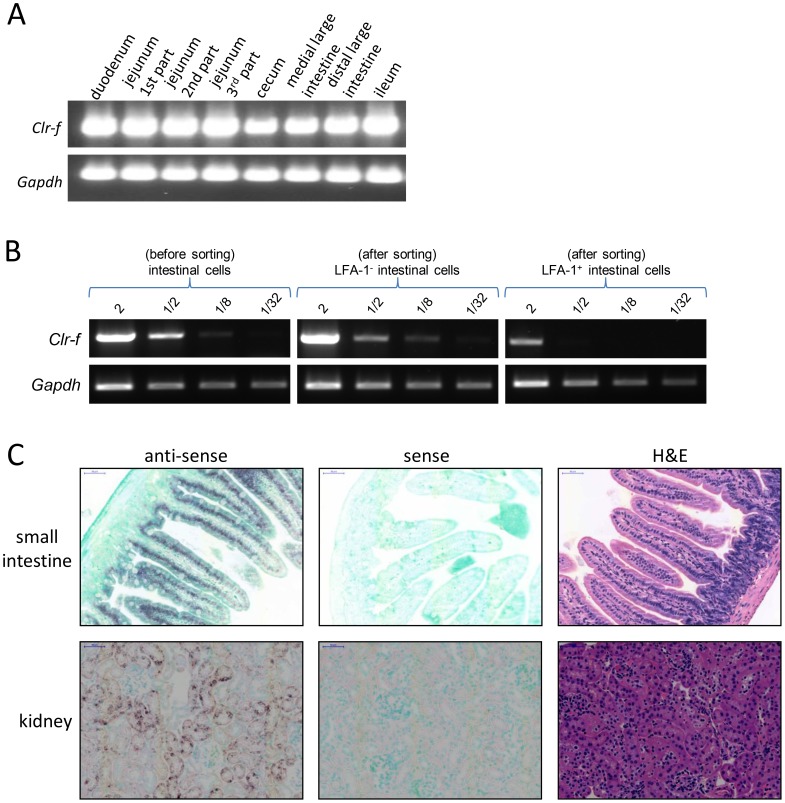
Figure 7. Clr-f is expressed in intestinal epithelial cells.
(A) Different sections of the small and large intestine from a PBS-perfused B6 mouse were separated and processed for RNA isolation. RT-PCR was performed on the resulting cDNAs with Clr-f-specific and Gapdh-specific primers. (B) Enriched Clr-f expression in non-lymphocytes of the intestine. A section of the small intestine was collagenase-digested and a single-cell suspension was prepared and stained with anti-LFA-1 mAb followed by sorting into lymphocyte and non-lymphocyte (epithelial) populations from which RNA was isolated and used for semi-quantitative Clr-f RT-PCR. The amount of cDNA in micrograms used in each reaction is indicated. (C) In situ hybridization reveals that Clr-f is abundantly expressed in intestinal epithelial cells and kidney tubular epithelium. DIG-labeled sense (control) and anti-sense RNA probes were used for hybridization to paraffin-embedded intestinal (jejunum) and kidney sections. Hybridization location of the probes was revealed by an alkaline-phosphatase-conjugated anti-DIG secondary followed by (brown) color substrate development. H&E staining of different section of the same organ reveals cellular organization of the tissue. The scale bars in the intestine and kidney sections indicate a length of 50 µm.