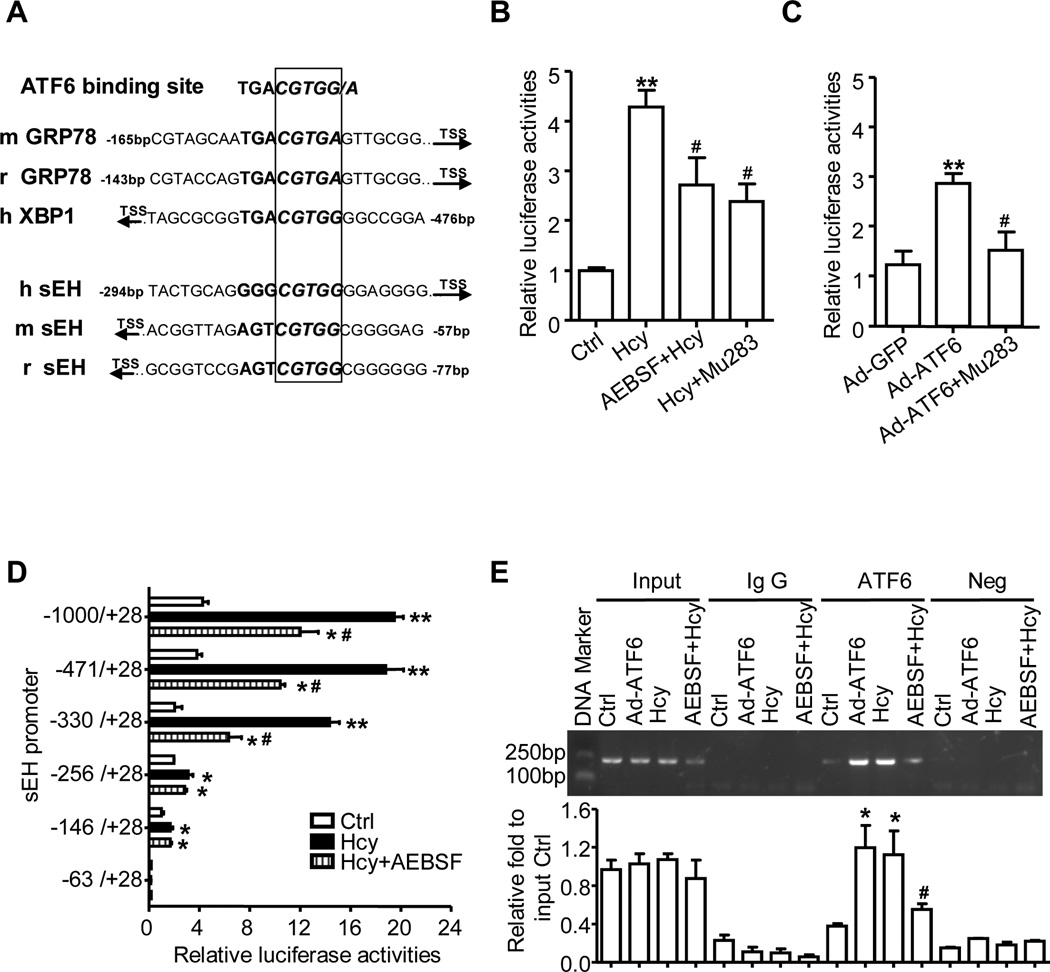
Figure 4. ATF6 binds to sEH promoter and activates promoter activity.
(A) Homology analysis of ATF6 binding site on the promoter of sEH among of human, rat and mouse by UCSC Genome Browser. Plasmids of sEH-1000-Luc or ATF6 site mutation (Mu283) were transfected into EA.hy926 cells, and then treated with Hcy, with or without AEBSF in (B), or infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-ATF6(N) for 24 hr in (C). Serial deletion constructs of sEH-Luc were transfected into EA.hy926 cells and treated with Hcy, with or without AEBSF for 24 hr (D). The β-gal plasmid was co-transfected as a transfection control. Promoter activities were measured by luciferase activity, which was normalized to that of β-galactosidase. Data are mean±SD of relative luciferase activities from 4 independent experiments. (E) ChIP assay involved use of anti-ATF6 antibody for immunoprecipitation in treated HUVECs; normal rabbit IgG was a control. Semi-quantitative PCR involved sEH promoter-specific primers to detect the binding of ATF6 to the sEH promoter region. Data are mean±SD of the percentage of input control from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Ctrl; #P<0.05 vs. Hcy or Ad-ATF6.